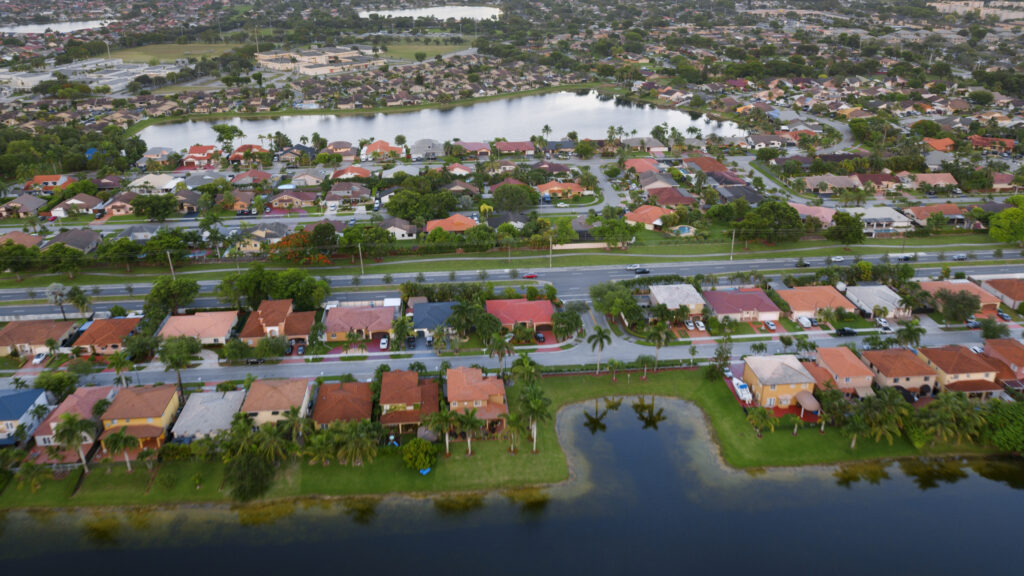
Sea Isle City, N.J., has regained its Class 3 rating under FEMA’s National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) Community Rating System (CRS) after a brief demotion last year. Being rated Class 3 enables the coastal town’s property owners to receive a 35 percent discount on their federal flood insurance.
CRS is a voluntary incentive-based program designed to encourage strong floodplain management. Class 1 is the highest rating, enabling residents to obtain a 45 percent reduction in their premiums. Class 10 indicates that a community doesn’t participate in CRS. To date, only two of the 1,500 participating communities nationwide have achieved the highest rating: Tulsa, Okla., and Roseville, Calif.
High ratings are not easy to obtain or maintain. Sea Isle City first reached Class 3 in 2018, and the rating was briefly lowered to Class 4 last year after points awarded to communities after Superstorm Sandy expired. The city quickly regained Class 3 status through additional flood-management activities.
In the mid-1990s, conditions were so bad for Sea Isle City that it was nearly ejected from the NFIP. If this had happened, property owners wouldn’t have had access to federal flood insurance. Neil Byrne, the city’s floodplain manager, construction official, building sub-code official, and zoning officer, attributes the improvement to strengthened zoning ordinances that require structures to be elevated higher than FEMA recommends, as well as investment in berms and bulkheads.
“The history of Sea Isle City going from facing expulsion from the NFIP to now leading the charge in the CRS in New Jersey is truly inspirational,” said Thomas Song, FEMA resiliency specialist. “What does not get enough attention is that success in the CRS program has to start with a strong understanding of the day-to-day compliance with NFIP requirements. It is extremely difficult to advance in CRS status without a strong foundation in floodplain-management practices.”
Achieving higher CRS rankings has become something of a friendly competition among coastal New Jersey towns, and only one other New Jersey community – Avalon – has a Class 3.
“Both Sea Isle City and Avalon have demonstrated their commitment in planning for future flooding, implementing higher building standards, and engaging in extensive public outreach,” Song said. “These efforts create an environment geared towards reducing flood damage and enhancing the safety and well-being of residents.”
As NFIP – through its Risk Rating 2.0 reforms – attempts to better align premium rates with risk, CRS discounts become even more significant to owners in flood-prone communities.
Last year, 17 Florida jurisdictions achieved Class 3 ratings. In Cutler Bay – a town on Miami’s southern flank with about 45,000 residents – the average premium dropped by $338. Citywide, that represented a savings of $2.3 million. In January 2024, Miami-Dade County became the latest municipality in the flood- and hurricane-prone state to achieve Class 3, leapfrogging from Class 5 due to the county’s flood-mitigation investments.
Meanwhile, back in New Jersey, Byrne says Sea Isle City hopes to become the state’s first Class 2 community.
“It’s very hard to get to the next level,” he said, but adds that flood pumps could help the city over the hump.
“Ninety-nine percent of our flooding is tidal flooding,” Byrne said, referring to inundation that happens during high tide events. “A lot of it goes away on its own, but we have little areas that need help getting the water out.”
About 90 percent of all U.S. natural disasters involve flooding. For decades, NFIP was practically the only available option for homeowners to obtain flood coverage. Before Risk Rating 2.0, however, coverage for higher-risk properties was often unfairly subsidized by lower-risk property owners.
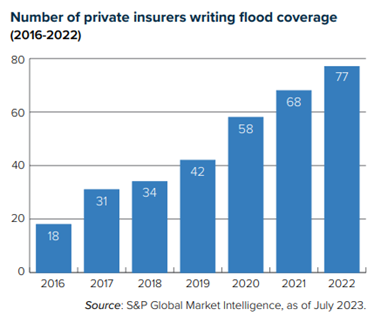
In recent years, improved data, analysis, and modeling have helped drive increased private-sector interest in flood risk. This, combined with the NFIP reforms, should foster a more competitive flood insurance market in which coverage is both more available and more fairly priced.
“Collective responsibility and multi-disciplinary collaboration are necessary to build resilience around climate-related perils like flood,” said Triple-I CEO Sean Kevelighan. “FEMA’s CRS program is just one example of how communities can make themselves safer and save money through targeted investments that reduce the likelihood and size of catastrophic losses.”
Learn More:
Triple-I “State of the Risk” Issues Brief: Flood
FEMA Reauthorization Session Highlights Importance of Risk Transfer and Reduction
Miami-Dade, Fla., Sees Flood-Insurance Rate Cuts, Thanks to Resilience Investment
FEMA Incentive Program Helps Communities Reduce Flood Insurance Rates for Their Citizens
Proposed Flood Zone Expansion Would Increase Need for Private Insurance