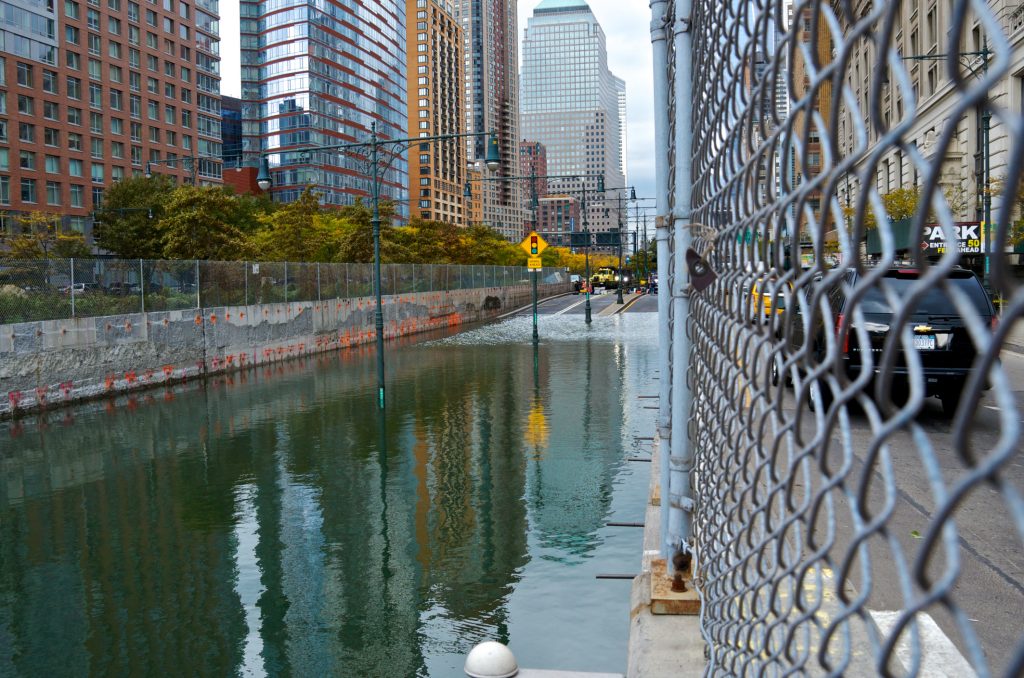
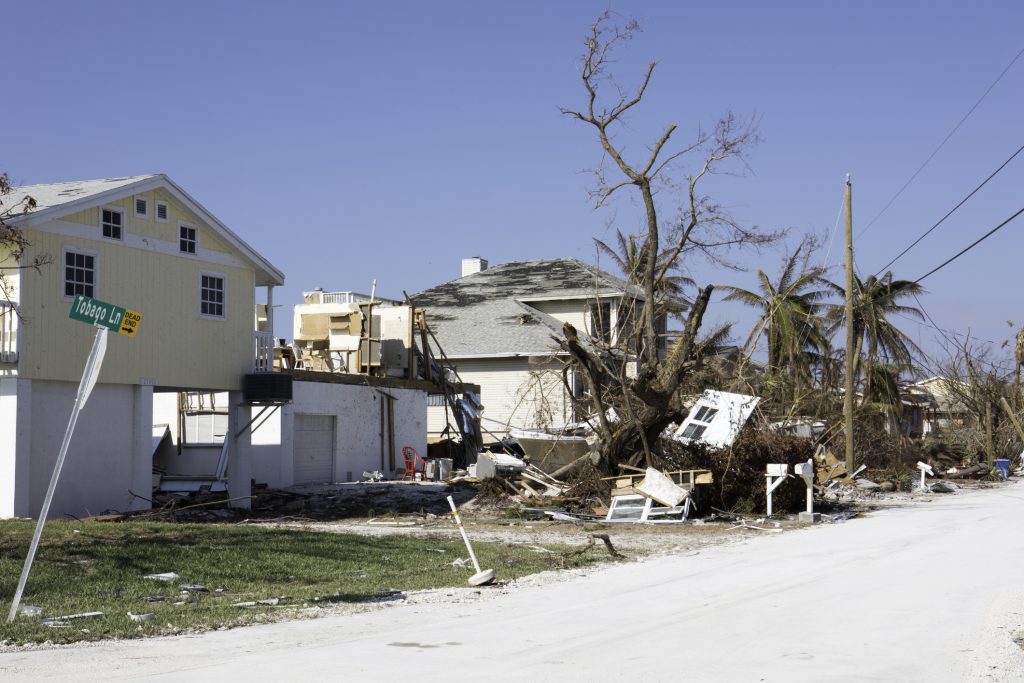
If there was a recurring theme in last week’s Senate Banking Committee hearing on reauthorization of FEMA’s National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), it was the need for:
- Congress to reauthorize NFIP, and
- Communities, businesses, and government at all levels to invest in mitigating flood risk and in improving resilience.
It’s important to amplify this message, especially in light of a recent proposal by Rep. Adam Schiff that would, among other things, disband NFIP and require property/casualty insurers to provide “all-risk policies” based on coverage thresholds and rating factors dictated by a board in which the insurance industry is only nominally represented. Last year’s budget uncertainty – in which a potential government shutdown was threatened – left open the very real possibility of funding for NFIP expiring if Congress failed to reach a deal.
“Federal policies and programs, including NFIP, are essential,” said Daniel Kaniewski, managing director, public sector, for Marsh McLennan in his testimony. “But all disasters are local, and so too are resilience investment decisions.”
Before joining Marsh McLennan, Kaniewski was the second-ranking official at FEMA, where he was the agency’s first deputy administrator for resilience.
“To increase the resilience of communities against the pervasive risk of flooding,” Kaniewski testified, “we believe that risk transfer— including from the NFIP, private flood insurance, reinsurance, and parametric insurance — should be paired with risk reduction.”
In this regard, Kaniewski emphasized NFIP’s Community Rating System (CRS), which encourages and rewards community floodplain management practices that exceed the NFIP’s minimum requirements. He cited Tulsa, Okla., as one of two U.S. communities to have achieved the highest CRS rating (the other is Roseville, Calif.), making residents eligible for the program’s greatest flood insurance discount of 45 percent.
Even without achieving the maximum rating, citizens save on flood insurance when their communities invest in resilience. For example, Miami-Dade County, Fla., recently became the latest jurisdiction in the hurricane- and flood-prone state to benefit from CRS program. The county’s new Class 3 rating will result in an estimated $12 million savings annually by giving qualifying residents and business owners in unincorporated parts of the county a 35 percent discount on flood insurance premiums.
Last year, 17 other Florida jurisdictions achieved Class 3 ratings. In Cutler Bay – a town on Miami’s southern flank with about 45,000 residents – the average premium dropped by $338. Citywide, that represented a savings of $2.3 million.
Unfortunately, only 1,500 communities nationwide participate in CRS, underscoring the importance of awareness-building, education, and collaboration.
Kaniewski also highlighted the opportunity presented by community-based catastrophe insurance (CBCI), which uses parametric insurance to provide coverage to local government entities that wish to cover a group of properties. Such programs enhance financial resilience by simultaneously providing affordable coverage and creating incentives for risk reduction.
“Our recent CBCI pilot in New York City was developed in partnership with the City of New York and several nonprofit and insurance industry partners and funded by the National Science Foundation,” Kaniewski said. “It provides a level of financial protection for low-to-moderate-income households that previously lacked flood insurance.”
Kaniewski called on other industries – such as finance and real estate – to encourage flood resilience investments, along with the insurance industry and all levels of government. He cited the recent roadmap for resilience incentives issued by the National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS) – funded by Fannie Mae and co-authored by representatives of a cross-section of “co-beneficiary industries” – that focused on residential structures prone to flooding. Triple-I subject-matter experts were co-authors on the NIBS project.
Sen. Tim Scott of South Carolina, committee co-chair – along with Sen. Sherrod Brown of Ohio – spoke from the perspective of a former insurance professional who has sold flood insurance about his state’s recent investment in mitigation.
“In 2023, the state’s budget included significant funding for mitigation efforts that would reduce flood damage from future storms,” Scott said.“Backing up that investment, the South Carolina Office of Resilience released a nationally praised Statewide Risk Reduction Plan, identifying the communities most vulnerable to floods and targeting mitigation resources to protect those residents. These are local solutions to local challenges – and they will make a huge difference in the lives of South Carolinians.”
While solutions that work in South Carolina might not work in other states, Scott said, “I’m confident that similar, locally based solutions and approaches could make a huge difference.”
Sen. Katie Britt of Alabama invited Kaniewski to elaborate on her state’s Strengthen Alabama Homes program, which provides grants and insurance discounts to homeowners who make qualifying retrofits to their houses. Britt cited research that found the program had “directly resulted in lower insurance premiums and higher home resale values.”
Kaniewski spoke in detail about Alabama’s efforts, including Strengthen Alabama Homes – which, he pointed out, is now being emulated by other states, including hurricane- and flood-prone Louisiana. He also cited by name the author of the research Britt referenced – Dr. Lars Powell, executive director of the Alabama Center for Insurance Information and Research at the University of Alabama and a Triple-I Non-resident Scholar – for producing “the first study that I’ve seen that gives empirical data — real evidence that mitigation pays.”
Steve Patterson, mayor of Athens, Ohio, described a range of nature-based solutions his city has taken – from rerouting the Hocking River, which runs through the middle of the city, to removing invasive plants and restoring native trees along the bank.
“That’s been very effective in reducing flooding in different neighborhoods throughout the city,” Patterson said. “There are a lot of things cities and villages can do.”
The work done by Athens – like green infrastructure work by the Milwaukee Metropolitan Sewerage District in Wisconsin and municipal entities – offers opportunities to reduce flood risk while improving quality of life for citizens. But, as Patterson points out, not all municipalities have the financial capacity to engage in such projects.
That is where the engagement of co-beneficiaries of resilience investment as partners becomes so crucial.
Learn More:
Miami-Dade, Fla., Sees Flood Insurance Rate Cuts, Thanks to Resilience Investment
Milwaukee District Eyes Expanding Nature-Based Flood-Mitigation Plan
Attacking the Risk Crisis: Roadmap to Investment in Flood Resilience
Proposed Flood Zone Expansion Would Increase Need for Private Insurance
FEMA Incentive Program Helps Communities Reduce Flood Insurance Rates for Their Citizens
FEMA Names Disaster Resilience Zones, Targeting At-Risk Communities for Investment