By Lewis Nibbelin, Contributing Writer, Triple-I
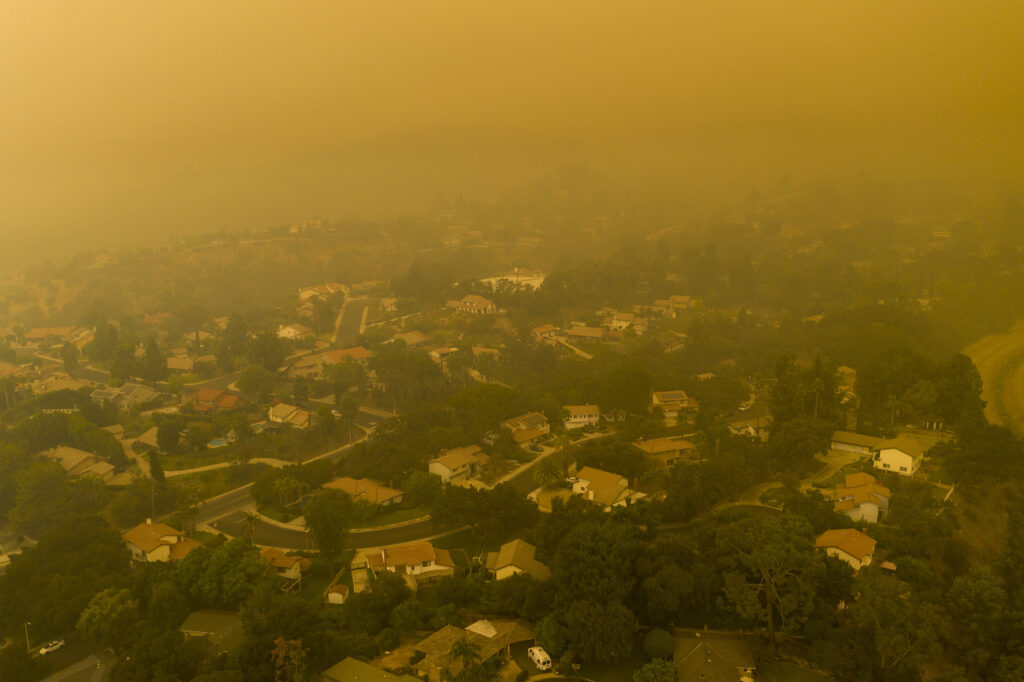
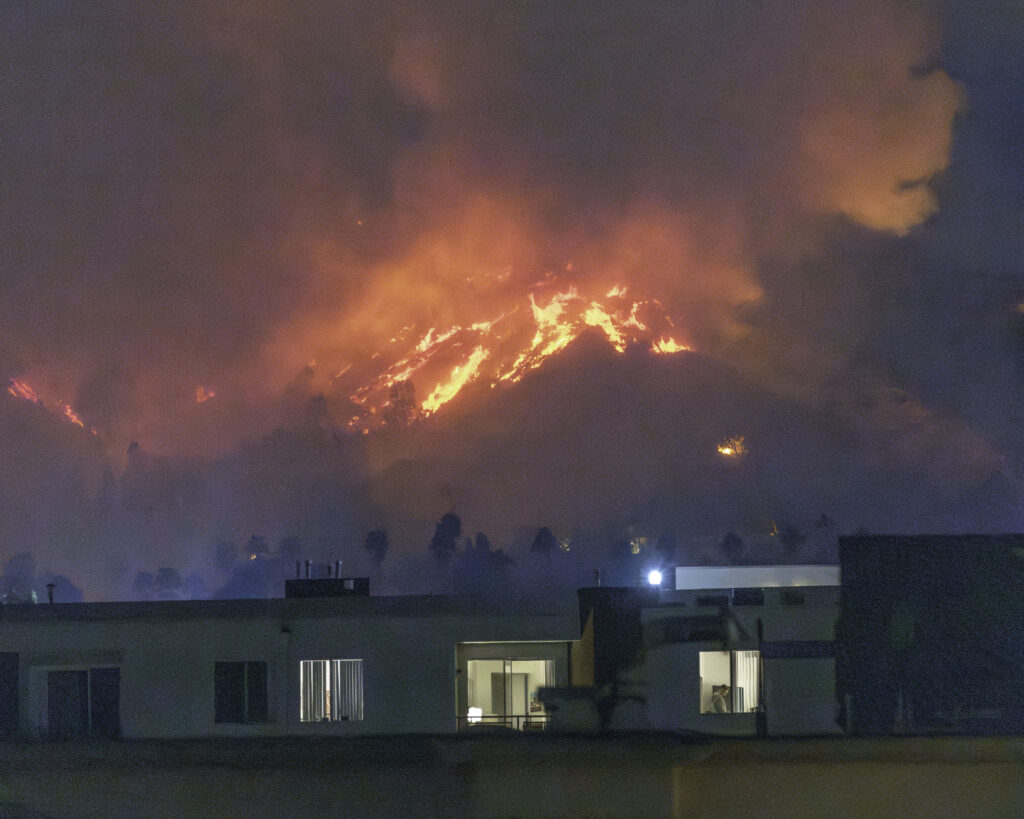
Two lawsuits filed in Los Angeles claim major California insurers colluded illegally to impede coverage in wildfire-prone areas, forcing homeowners into the state’s last-resort FAIR Plan. Accusing carriers of violating antitrust and unfair competition laws, the two suits exemplify an ongoing disconnect between public and insurer perceptions of insurance market dynamics, exacerbated by legislators’ resistance to accommodating the state’s evolving risk profile.
An untenable situation
Both suits claim the insurers conspired to “suddenly and simultaneously” drop existing policies and cease writing new ones in high-risk communities, deliberately pushing consumers into the FAIR Plan. Left underinsured by the FAIR Plan, the plaintiffs argue they were wrongfully denied “coverage that they were ready, willing, and able to purchase to ensure that they could recover after a disaster,” Michael J. Bidart, who represents homeowners in one of the cases, said in a statement.
Established in response to the 1965 Watts Rebellion, the California FAIR Plan provides an insurance option for homeowners unable to purchase from the traditional market. Though FAIR Plans offer less coverage for a higher premium, they cover properties where insurance protection would otherwise not exist. California law requires licensed property insurers to contribute to the FAIR Plan insurance pool to conduct any business within the state, meaning they share the risks associated with those properties.
Intended as a temporary solution until homeowners can secure policies elsewhere, the FAIR Plan has become overwhelmed in recent years as more insurers pull back from the market. As of December 2024, the FAIR plan’s exposure was $529 billion – a 15 percent increase since September 2024 (the prior fiscal year end) and a 217 percent increase since fiscal year end 2021. In 2025, that exposure will increase further as FAIR begins offering higher commercial coverage for farmers, homebuilders, and other business owners.
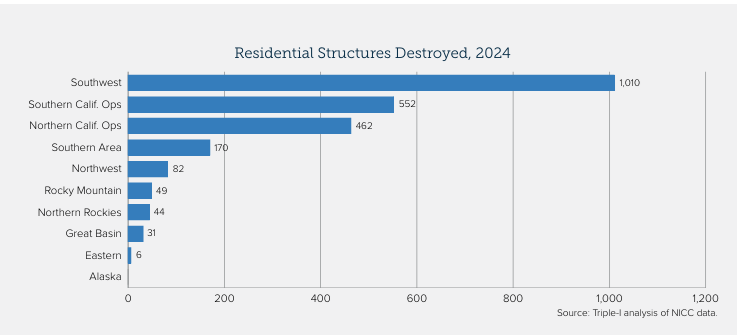
With a policyholder count that has more than doubled since 2020, the FAIR Plan faces an estimated $4 billion total loss from the January fires alone.
Out of touch regulations
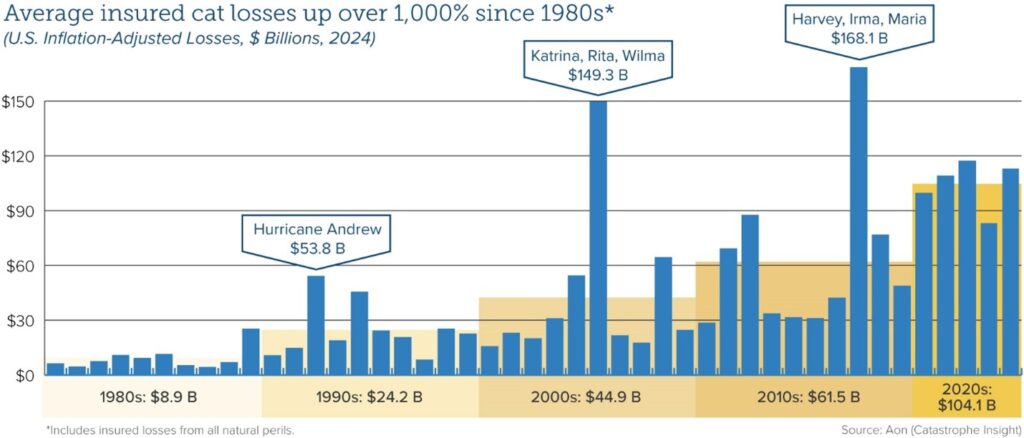
Homeowners are understandably frustrated with dwindling coverage availability, which currently afflicts many other disaster-prone states. Supply-chain and inflationary pressures, which could intensify under oncoming U.S. tariff policies, help fuel the crisis. But California’s problems stem largely from an antiquated regulatory measure that severely constrains insurers’ ability to manage and price risk effectively.
Despite a global rise in natural catastrophe frequency and severity, regulators have applied the 1988 measure, Proposition 103, in ways that bar insurers from using advanced modeling technologies to price prospectively, requiring them to price based only on historical data. It also blocks insurers from incorporating reinsurance costs into their prices, forcing them to pay for these costs from policyholder surplus and/or reduce their presence in the state.
Insurers must adjust their risk appetite to reflect these constraints, as they cannot profitably underwrite otherwise. Underwriting profitability is essential to maintain policyholder surplus. Regulators require insurers to maintain policyholder surplus at levels that ensure that every policyholder is adequately protected.
Restricting insurers’ use of prospective data, however, inhibits risk-based pricing and weakens policyholder surplus, facilitating policy nonrenewals and, in serious cases, insolvencies.
Insurance Commissioner Ricardo Lara implemented a Sustainable Insurance Strategy to mitigate these trends, including a new measure that authorizes insurers to use catastrophe modeling if they agree to offer coverage in wildfire-prone areas. The strategy has garnered criticism from legislators and consumer groups, one of whom is suing Lara and the California Department of Insurance over a 2024 policy aimed at expediting insurance market recovery after an extreme disaster.
“Insurers are committed to helping Californians recover and rebuild from the devastating Southern California wildfires,” Denni Ritter, the American Property Casualty Insurance Association’s department vice president for state government relations, said in a statement about the suit. “Insurers have already paid tens of billions in claims and contributed more than $500 million to support the FAIR Plan’s solvency – even though they do not collect premiums from FAIR Plan policyholders.”
A call for collective action
Litigation prolongs – it does not alleviate – California’s risk crisis. Government has a crucial role to play in addressing it, from adopting smarter land-use planning regulations to investing in long-term resilience solutions.
For instance, Dixon Trail, a San Diego County subdivision dubbed the country’s first “wildfire resilient neighborhood,” models the Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety (IBHS) standards for wildfire preparedness, but not at a cost attainable to most communities, and few local governments incentivize them. Launched by state legislature in 2019, the California Wildfire Mitigation Program is on track to retrofit some 2,000 houses along these guidelines, with the goal of solving how to fortify homes more quickly and inexpensively. Funded primarily by FEMA’s Hazard Mitigation Assistance Grant program, the pilot has thus far avoided the same cuts befalling FEMA’s sister programs under the Trump Administration.
Regardless of what legislators do, California homeowners’ insurance premiums will need to rise. The state’s current home and auto rates are below average as a percentage of median household income, reflecting a combination of the increased climate risk and of the regulatory limitations preventing insurers from setting actuarially sound rates. Insurance availability will not improve if these rates persist.
To quote Gabriel Sanchez, spokesperson for the state’s Department of Insurance: “Californians deserve a system that works – one where decisions are made openly, rates reflect real risk, and no one is left without options.” Insurers do not wield absolute control over that system, and neither do legislators, regulators, consumer advocates, or any other singular group. Confronting the root causes of these issues – i.e., the risks – rather than the symptoms is the only path towards systemic change.
Learn More:
Despite Progress, California Insurance Market Faces Headwinds
California Insurance Market at a Critical Juncture
California Finalizes Updated Modeling Rules, Clarifies Applicability Beyond Wildfire
How Proposition 103 Worsens Risk Crisis In California
Tariff Uncertainty May Strain Insurance Markets, Challenge Affordability
Issues Brief: California Struggles to Fix Insurance Challenges (Members only)
Issues Brief: Wildfire: Resilience Collaboration & Investment Needed (Members only)