By Lewis Nibbelin, Research Writer, Triple-I
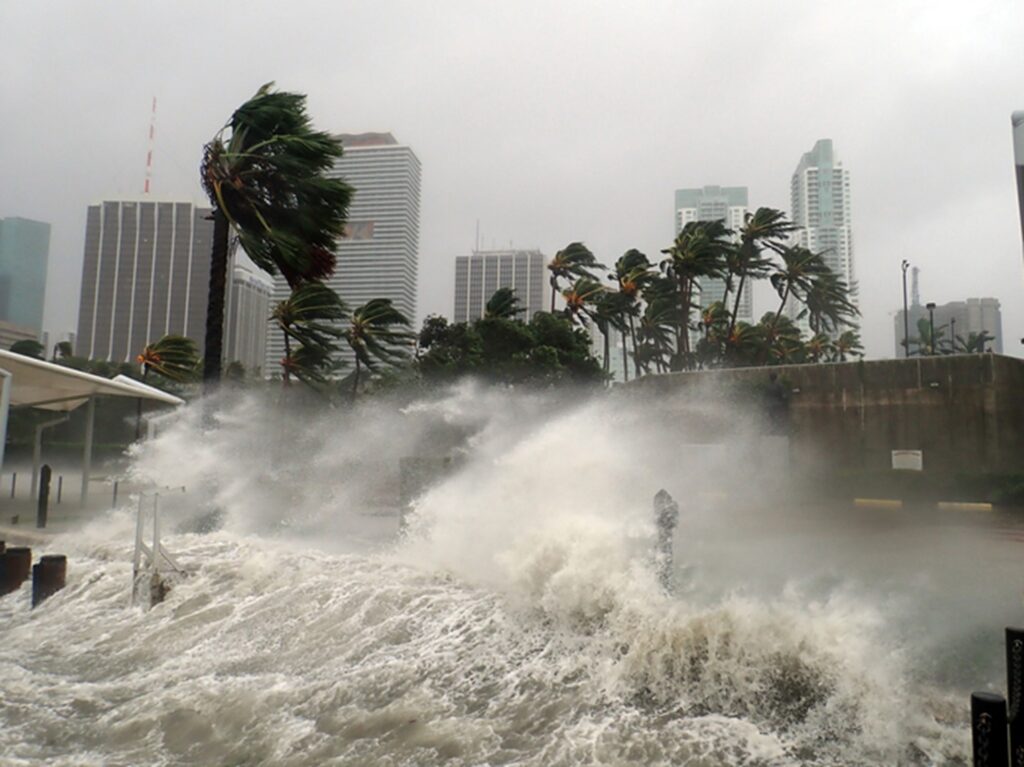
Though producing no U.S. landfalls for the first time in a decade, the 2025 Atlantic hurricane season generated deadly tropical storms, above-average days of major hurricane activity, and millions in economic losses, underscoring the enduring community preparedness required against this evolving peril.
Among the five hurricanes that did form, four reached Category 3 strength or higher, including three Category 5 storms – marking only the second year on record that more than two such storms occurred in the Atlantic. A new Triple-I Issues Brief examines their impacts and how they align with emerging climate and weather trends, particularly within inland areas hit by flooding from remnants of the storms.
Flood exposure spreads inland
While not to the scale of U.S. hurricanes in 2024, the year’s tropical storms were similarly destructive, with remnant moisture from Tropical Storm Chantal contributing to $500 million in damage, Gallagher Re estimates. In many affected North Carolina counties, less than 1 percent of households were covered by the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), highlighting a growing flood protection gap in areas once considered low-risk.
Demographic shifts also play a crucial role in the devastation as more people move into harm’s way and build their homes bigger and more expensive than before. While various flood-prone areas along the coasts lost more residents than they gained in 2024 – for the first time since 2019 – it is critical to remind home and business owners about rising flood risks throughout the country and the importance of staying protected.
Stronger, wetter weather
Warming oceans also fuel “rapid intensification,” or an increase in maximum sustained winds by at least 35 mph in a 24-hour period. Since 1980, over 80 percent of landfalling U.S. hurricanes – altogether costing at least $5 billion in damages – underwent rapid intensification at some point during their lifecycle, according to a 2025 American Geophysical Union (AGU) study.
Describing rapid intensification events as “a pronounced increasing trend,” AGU study coauthor Dr. Phil Klotzbach – a senior research scientist in the Department of Atmospheric Science at Colorado State University and Triple-I non-resident scholar – said such storms “tend to weaken at a slower rate as they move inland,” compounding challenges for residents who “aren’t necessarily as prepared as they should be.”
Hurricane Melissa – 2025’s strongest and deadliest storm – showcased the toll from this mounting intensity. Claiming more than 100 lives across the Caribbean, Melissa rapidly intensified before hitting Jamaica as a Category 5 hurricane, becoming one of the fastest-intensifying Atlantic storms ever recorded and the most powerful hurricane to make landfall in the country’s history.
Cutting-edge analytics
As advances in computing power and data collection have improved traditional tools in recent years, forecasters and insurers have built up their arsenal to combat the unpredictability of climate and weather risks. For instance, barometric pressure – found both more accurate and easier to gauge than the wind speeds traditionally used to predict storm damage – served as the primary trigger for a $150 million parametric policy for Jamaica which paid out in full after Hurricane Melissa.
“Displaying the kind of predictive power that can help insurers price risk and mitigate costly claims, these technologies can inform conversations at all levels to encourage investment in resilience,” the brief states.
Learn More:
Storm-Resistant Roof Efforts Gain Ground
Jamaica Payout Spotlights Potential of Parametric
Resilience Investment Payoffs Outpace Future Costs More Than 30 Times
‘Predict and Prevent’ Insurance Model Can Restore Consumer Trust: Nationwide
Resilience Investments Paid Off in Florida During Hurricane Milton