By Lewis Nibbelin, Research Writer, Triple-I
Amid federal funding and staffing cuts to major science agencies last year, various nonprofit organizations stepped up to maintain their essential climate and weather research. Such risks may become increasingly difficult to predict and prevent, however, as key agencies, such as the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), remain targets for disinvestment or termination.
Private sector takes charge
In the spring of 2025, the federal administration attempted to rescind tens of billions of dollars in research and hazard mitigation grants, leaving many programs – like FEMA’s Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities (BRIC) program – in legal limbo as legislators continue to debate their futures. Alongside funding delays and cancellations, mass firings led to the shuttering of several climate and weather information resources – until private associations and researchers mobilized to revive them.
Former NOAA staffers, for instance, regrouped to rescue the organization’s climate.gov website, which attracted nearly one million visitors per month – including teachers, policymakers, and media outlets – before being dismantled last June. Under a new domain, the site will both restore deleted information and resume tracking and explaining the effects of climate risk to public audiences, relying exclusively on nonprofit funding, according to project director Rebecca Lindsey in an interview with NPR.
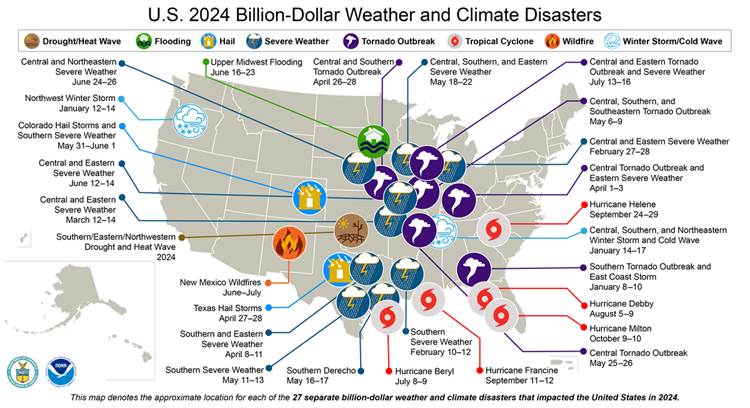
Similarly, nonprofit Climate Central recently released its first billion-dollar weather and climate disaster report since assuming responsibility for that dataset, which former NOAA climatologist Adam Smith continues to oversee. Beyond rebuilding NOAA’s database, the organization aims to expand upon it in the coming years to track smaller catastrophes, providing insurers and other stakeholders more reliable information to understand individual disasters.
An initiative spearheaded by the American Geophysical Union (AGU) and the American Meteorological Society (AMS) is now aiming to help fill research gaps left by the elimination of the National Climate Assessment (NCA), a series of congressionally mandated reports published since 2000 to inform climate risk mitigation strategies for municipalities and businesses. Though not intended to replace NCA, the new data collection “provides a critical pathway for a wide range of researchers to come together and provide the science needed” to “ensure our communities, our neighbors, our children are all protected and prepared,” said AGU president Brandon Jones.
Grassroots efforts to archive federal climate databases and tools before they disappear have also gained traction around the globe to ensure these resources remain publicly available. The nonprofit Open Environmental Data Project, for example, saved a now-deleted tool to identify communities disproportionately impacted by climate and weather risks through its Public Environmental Data Project.
Crucial agencies under scrutiny
While the latest government spending package has largely spared science funding from further reductions, the Trump administration had proposed cuts amounting to a 21 percent drop from fiscal 2025 levels. Other agencies face potential dissolution, particularly NCAR – widely considered the largest federal climate research program in the U.S.
Managed by the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) in collaboration with the National Science Foundation (NSF), NCAR houses advanced computing and modeling systems to support weather forecasts, mitigation planning, flood mapping, and other datasets needed across the transportation, engineering, utility, and risk and insurance industries.
Describing NCAR’s research as critical to “protecting lives and property, supporting the economy, and strengthening national security,” UCAR president Antonio Busalacchi said in a statement that “any plans to dismantle NSF NCAR would set back our nation’s ability to predict, prepare for, and respond to severe weather and other natural disasters.”
“NCAR datasets have been vital in improving our understanding of the atmosphere and ocean,” said Phil Klotzbach, lead author of Colorado State University’s seasonal hurricane forecasts and Triple-I Non-Resident Scholar. “These tools have been critical input to CSU’s seasonal hurricane forecasts for over 25 years.”
NCAR’s pending fate coincides with a recent study from the University of Florida that suggests the budget cuts in part reflect pervasive distrust in scientific institutions, necessitating stronger efforts to communicate the value of scientific work to the public. But as more independent groups take on the responsibilities once affiliated with federal organizations, building public relationships may prove even more challenging, posing uncertain implications for the future of climate and weather data as a whole.
Learn More:
Inflation, Replacement Costs, Climate Losses Shape Homeowners’ Insurance Options
End of Federal Shutdown Revives NFIP — For Now
Texas: A Microcosm of U.S. Climate Perils
Some Weather Service Jobs Being Restored; BRIC Still Being Litigated
BRIC Funding Loss Underscores Need for Collective Action on Climate Resilience
Claims Volume Up 36% in 2024; Climate, Costs, Litigation Drive Trend