By Lewis Nibbelin, Research Writer, Triple-I
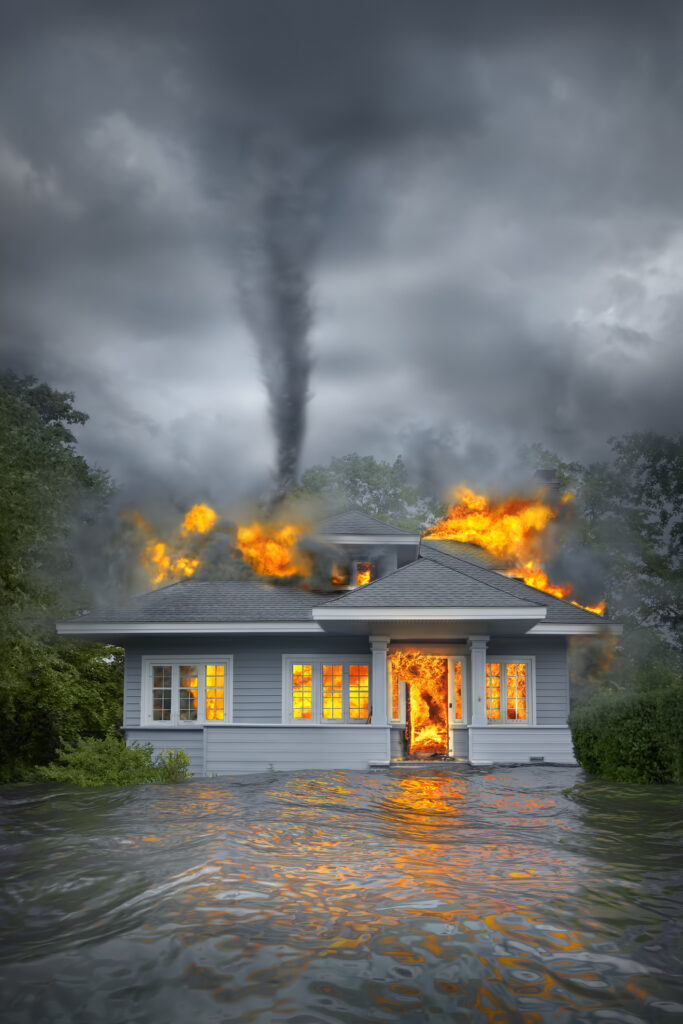
As communities nationwide rebuild after last year’s 23 billion-dollar weather and climate disasters, many must weigh the benefits of climate-resilient construction over the immediate financial burdens, logistical obstacles, and other constraints associated with recovery. Perceived cost of these building standards poses another challenge, underscoring a widespread awareness gap that impedes adoption.
A new report from Crawford & Company explores how facilitating resilient construction became a major focus among claims leaders across the globe, as part of a greater industry shift to center sustainability in claims decision-making. Based on interviews and survey responses from a cross-section of carrier and broker partner organizations, the report highlights the growing momentum to incentivize home upgrades due to their long-term cost savings, with such initiatives largely backed by insurers themselves.
“When we can collaborate at an industry level and converge on some best practices, we’re going to create a lot more benefit for the effort that we put in,” said Pat Van Bakel, the firm’s chief commercial and strategy officer, in a recent Executive Exchange with Triple-I CEO Sean Kevelighan. “My advice is to be practical: think about what we can do that is going to drive some impact and then build from there.”
Though differing economic, political, and legal pressures shape regional approaches to resilience, Van Bakel explained that “most organizations have referenced sustainability or resiliency in their corporate strategy,” with 70 percent of respondents identifying sustainability considerations as impactful in their adjudication and resolution process. Many mentioned integrating programs to make homes more resilient to severe weather, aligning with broader industry trends to prioritize sustainable restoration over replacement.
While house upgrades to voluntary FORTIFIED standards, for instance, remain relatively affordable, adoption skyrocketed under insurer-funded programs that offer homeowners grants to retrofit their roofs along such guidelines, with completed retrofits earning policyholders steep premium discounts. Developed by the Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety (IBHS), the construction method has demonstrated success in reducing severe storm and hurricane damage, prompting a burgeoning number of state governments to help launch their own programs.
Beyond risk reduction, “what they’ve found in those areas is that the home values have started going up and the prices of insurance have started going down,” Kevelighan said, creating an “economic flywheel to incentivize people to take action.”
Similar efforts are underway in Dallas, Tex., Kevelighan added, as Triple-I works to establish “a property-based resiliency score” that homeowners can use to “tap into a revolving loan and grant fund that allows them to get the financial means” for needed home improvements.
Premium discounts are also attainable for California residents who meet specific standards for wildfire mitigation, many of whom are pursuing certification through the IBHS Wildfire Prepared Home program. Initiated by the state’s updated “Safer from Wildfires” regulations, the discounts offer some relief for the thousands of Los Angeles homes still awaiting reconstruction after last year’s devasting wildfires in the county.
Aerial images of disaster-struck areas “bring to life the value” of these initiatives, Van Bakel said, noting that “you can see the benefit of putting resiliency into the infrastructure when there’s no other way to explain how one structure can look relatively unscathed and one right next door to it is flattened or burned to the ground, depending on the peril.”
Crawford & Company’s report further emphasizes the claims industry’s role in helping “connect the dots” for policyholders on the resources available to them, including the accessibility of resilience funding and their code upgrade coverage. While 69 percent of respondents indicated sustainability is important to their customers, the demand for such measures has yet to fully translate to public education and coordinated industry support.
As insurers increasingly navigate these efforts, Van Bankel encourages the industry to “follow what I would describe as the demand pull, rather than trying to create demand, and I think we’ll be a lot more successful.”
Learn More:
Flash Floods Set Records in 2025, Inland Risk Surges
Climate Nonprofits Take Responsibility for Terminated U.S. Databases
Storm-Resistant Roof Efforts Gain Ground
Resilience Investment Payoffs Outpace Future Costs More Than 30 Times
Study Supports Defensible Space, Home Hardening as Wildfire Resilience ToolsStudy Touts Payoffs from Alabama Wind Resilience Program