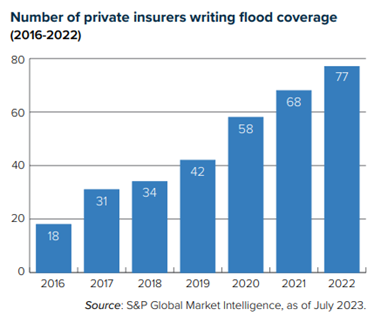
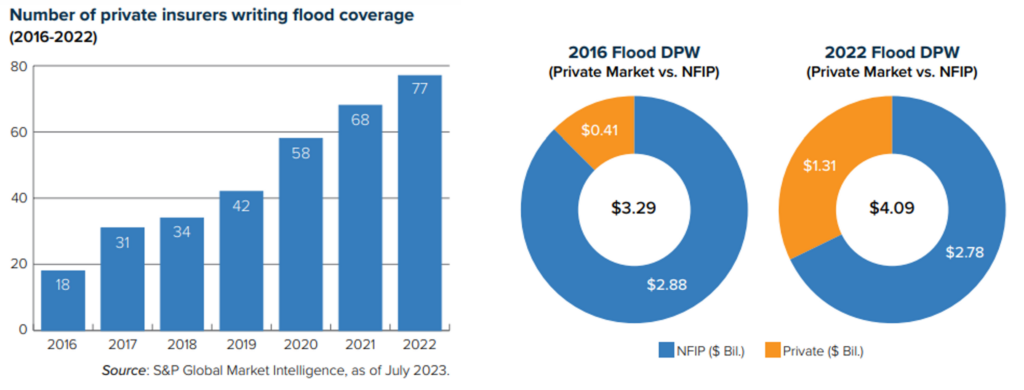
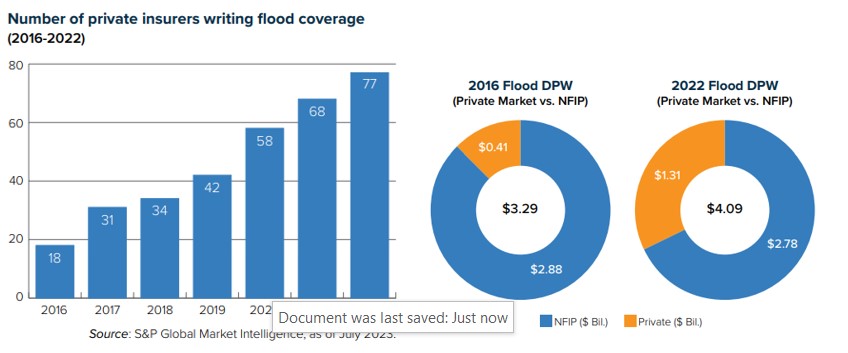
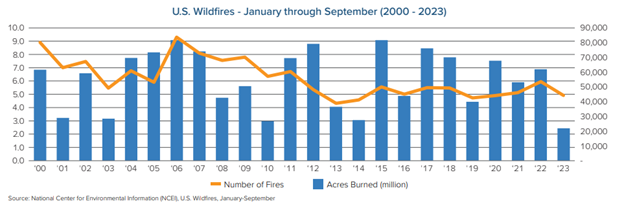
William Nibbelin, Senior Research Actuary, Triple-I
The recent National Council on Compensation Insurance (NCCI) Annual Insights Symposium (AIS) in Orlando, Fla., provided important context and clarity around the state of the workers compensation line of business. As a new senior research actuary for Triple-I, my prior knowledge of this line could best be summarized by the following words from one peer-reviewed study of a reserving project I conducted more than two decades ago: Long-tail, unprofitable.
I recently assumed responsibility for forecast modeling of the property/casualty industry, which includes workers comp. In this role, I’d seen the line’s 2023 net combined ratio at 87 – the lowest (ie., most profitable) in the past five years. But I did not yet have deep understanding of the underlying trends driving these numbers.
I saw the AIS as an opportunity to gain that knowledge, and the event delivered.
The net combined ratio of 87 – as reported by Triple-I using National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) data sourced by S&P Global Market Intelligence – was also the ninth straight calendar year in a row under 100. According to NCCI, the success of the workers comp line in recent years represents the convergence of three factors:
- Payroll increases
- Moderate severity increases, and
- Larger-than-expected frequency declines.
“The overall numbers for workers compensation show a financially healthy system,” said Donna Glenn, NCCI’s chief actuary.
Payroll increases
The line’s 2023 direct written premium (DWP) increased 2.6 percent nationally – due primarily to another strong year of payroll growth at 6.2 percent, according to NCCI.Rising wages contributed the most to that figure, with increases in all industry sectors resulting in a combined wage growth of 3.9 percent. Improved job creation contributed 2.3 percent, with all sectors except transportation and warehousing seeing increased employment. Payroll growth was partially offset by state-approved premium rate decreases.
Moderate severity increases
Claim severity remains moderate year over year, at 3 percent in 2023, despite indemnity claim severity at 5 percent. Medical claim severity for 2023 trended at a low 2 percent, in line with the 20-year trend of 1.8 percent and below the 3.5 percent in 2022. Medical claims less than $500,000 increased 5 percent; however, claims above $500,000 decreased 16 percent, driven primarily by several large losses in 2022.
Also, more states have adopted physician medical fee schedules from 2012 to 2022, which has shifted medical cost category shares from more expensive inpatient claims to outpatient claims, as well as lower drug claims. Outpatient claims increased from 23 percent of all claims to 27 percent and drug claims decreased from 12 percent to 7 percent of all claims.
Larger-than-expected frequency declines
Overall claim frequency decreased 8 percent in 2023, compared to the 20-year average decrease of 3.4 percent. Workers compensation claims frequency has only increased twice in the past 20 years – once in 2010 from the destabilization in the construction sector in 2009 and again in 2021 from COVID-19 impacts in 2020.
From 2015 to 2022, workers comp claims frequency benefited from workplace safety improvements and technology advances, which helped the decline in all cause of injury categories, including the two largest shares of strain and slip/falls. During this same period, the largest decline in claim frequency by part of the body was in lower-back claims. Finally, the recent slowing employment market churn has also improved claim frequency as claims decline when job tenure rises.
Stephen Cooper, senior economist at NCCI, speaking on the state of the economy and its impact on workers comp, said job growth and steadily increasing wage rates continue to favor the workers compensation system. He also gave an overview of the contribution to labor force by age and generation from 1980 to 2030, including changes in claim share from 2020 actuals to 2030 forecasts. Overall, the double-digit growth in labor force of 24 percent in 2000 over 1980 and 18 percent in 2020 over 2000 is expected to fall to only 4 percent in 2030 over 2020.
The only age group with an expected increasing contribution to the labor force from 2020 to 2030 are those age 65 and older. The contribution to labor force for the age group 16 to 24 is expected to remain flat from 2020 to 2030 however their representative share of Workers Compensation claims has the largest expected increase from 9% to 11 percent.
Beyond the numbers
The symposium provided valuable insight into several factors affecting workers comp, including the role of AI and innovation in workplace safety technology. In a panel moderated by Damian England, NCCI’s executive director of affiliate services, the audience got to see a demonstration of AI camera monitoring of warehouse employee activity and the use of wearable technology to highlight improper lifting techniques.
“It is clear that safety technologies will be a vital part of future safety initiatives,” England said. “They may even be a gamechanger for evaluating and improving workplaces and reducing injuries.”
AIS also touched on challenges facing today’s workers, from climate to mental health.
“Our new NCCI research shows worker injuries increase by as much as 10 percent on very hot days, as well as on wet and freezing days, compared to mild weather,” said Patrick Coate, NCCI senior economist. “High temperatures impact construction and other outdoor workers most, while cold and wet weather leads to a lot more slip and fall injuries.”
Anae Myers, assistant actuary at NCCI, focused on the difference between claims that include mental health diagnosis versus those that do not.
“New research from NCCI shows that claims exceeding $500,000 are 12 times more likely to be diagnosed with an associated mental condition during the course of treatment, underscoring the potential for the impact of mental health in large claims,” Myers said.
I left the conference with a better understanding of workers comp rate making and the indices to track for future forecasts. Many thanks to Cristine Pike and Madison White at NCCI for their hospitality and guidance, as well as to all the attendees who patiently provided their expertise and generously offered their support when I introduced myself to them and to this stunning line of insurance.