A climate nonprofit plans to revive a key federal database tracking billion-dollar weather and climate disasters that the Trump Administration stopped updating in May, Bloomberg reported.
The database captures the financial toll of increasingly intense weather events and was used by insurers and others to understand, model, and predict weather perils across the United States. Dr. Adam B. Smith, the former NOAA climatologist who spearheaded the database for more than a decade, has been hired to manage it for the nonprofit, Climate Central.
NOAA in May announced it would stop tracking the cost of the country’s most expensive disasters, those which cause at least $1 billion in damage – a move that would leave insurers, researchers, and government policymakers with less reliable information to help understand the patterns of major disasters like hurricanes, drought or wildfires, and their economic consequences.
Climate Central plans to expand beyond the database’s original scope by tracking disasters as small as $100 million and calculating losses from individual wildfires, rather than simply reporting seasonal regional totals.
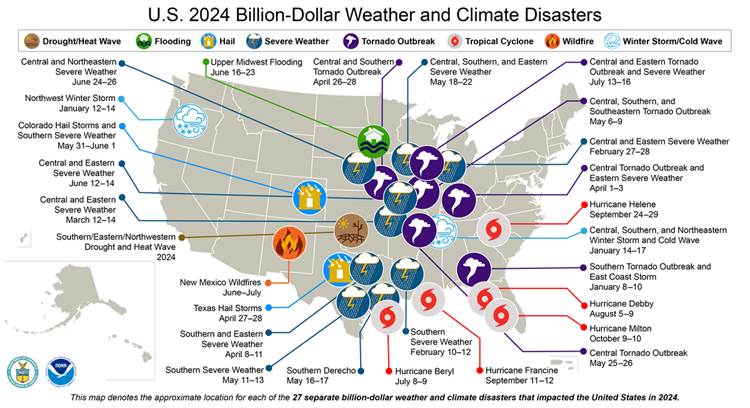
A record 28 billion-dollar disasters hit the United States in 2023, including a drought that caused $14.8 billion in damages. In 2024, 27 incidents of that scale occurred. Since 1980, an average of nine such events have struck in the United States annually.
This summer – amid deadly wildfires and floods – the Trump Administration has appeared to be rolling back some of its DOGE-driven NOAA funding cuts. NOAA recently announced that it would be hiring 450 meteorologists, hydrologists, and radar technicians for the National Weather Service (NWS), after having terminated over 550 such positions in the already-understaffed agency in the spring.
In addition, the administration’s announced termination of the Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities (BRIC) program — run by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) — has been held up by a court injunction while legislators debate its future. Congress established BRIC through the Disaster Recovery Reform Act of 2018 to ensure a stable funding source to support mitigation projects annually. The program has allocated more than $5 billion for investment in mitigation projects to alleviate human suffering and avoid economic losses from floods, wildfires, and other disasters.
Regarding the rescue of the NOAA dataset, Colorado State University researcher and Triple-I non-resident scholar Dr. Phil Klotzbach said, “The billion-dollar disaster dataset is important for those of us working to better understand the impacts of tropical cyclones. It uses a consistent methodology to estimate damage caused by natural disasters from 1980 to the present and was a critical input to our papers investigating the relationship between landfalling wind, pressure and damage. I’m very happy to hear that this dataset will continue!”
Learn More:
Some Weather Service Jobs Being Restored; BRIC Still Being Litigated
2025 Cat Losses to Date Are 2nd-Costliest Since Records Have Been Kept
CSU Sticks to Hurricane Season Forecast, Warns About Near-Term Activity
Russia Quake Highlights Unpredictability of Natural Catastrophes
Texas: A Microcosm of U.S. Climate Perils
Louisiana Senator Seeks Resumption of Resilience Investment Program
BRIC Funding Loss Underscores Need for Collective Action on Climate Resilience










