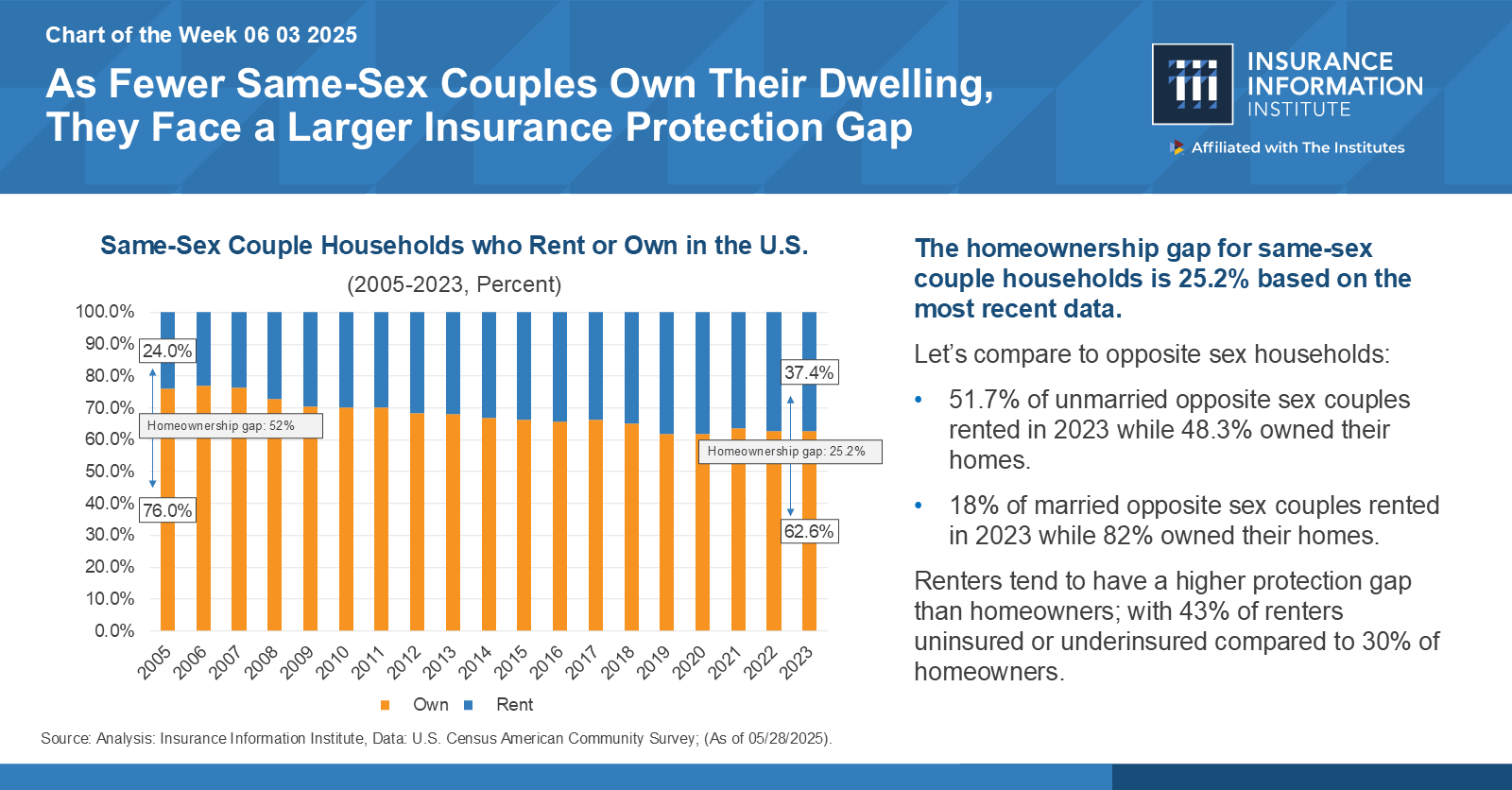
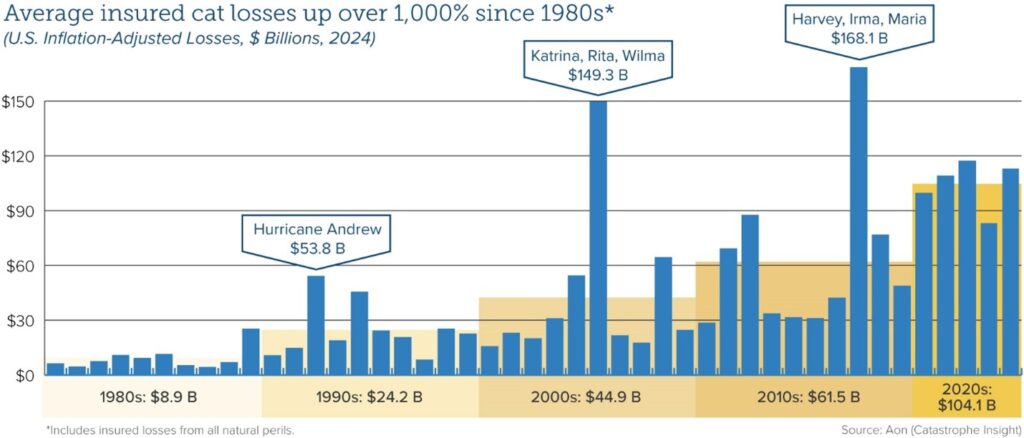
By Lewis Nibbelin, Contributing Writer, Triple-I
Identifying key risk trends amid an increasingly complex risk landscape was a dominant theme throughout Triple-I’s 2025 Joint Industry Forum – particularly during the panel spotlighting some of the insurance industry’s C-suite leaders.
Moderated by CNBC correspondent Contessa Brewer, the panel consisted of:
- J. Powell Brown, president and CEO of Brown & Brown Inc.;
- John J. Marchioni, chairman, president, and CEO of Selective Insurance Group;
- Susan Rivera, CEO of Tokio Marine HCC (TMHCC); and
- Rohit Verma, president and CEO of Crawford & Co.
Their discussion provided insight into how insurers can transform these uncertainties into opportunities for business development and for cultivating deeper connections with consumers.
Recouping policyholder trust
Given the volatility of the current risk environment – exacerbated by various ongoing geopolitical conflicts and the rising frequency and severity of natural catastrophes – it is more imperative than ever to reaffirm the intrinsic human element of insurance, the panelists agreed.
“That’s one of the most underappreciated aspects of our industry,” Marchioni said. “We make communities safer and put people’s lives and businesses back together after an unexpected loss. Being the calming force when you have unsettling events like this happen around the world is a big part of what we do.”
Yet prevailing public perception continues to indicate otherwise, even as insurers report repeated losses or nominal profits compared to other industries.
“The insurance industry may be the only industry where record profits are a problem,” CNBC’s Brewer added, because consumers tend to “not care whether it’s coming from your investments, or whether it’s coming from your underwriting business or your reinsurance. They just hear that you’re making record profits.”
Brown noted that consumer mistrust derives, in part, from “a very active plaintiffs’ bar,” which the American Tort Reform Association estimates spent over $2.5 billion for nearly 27 million ads across the United States last year. He further discussed how, though the average homeowners’ insurance premium rate in Florida will increase this year, his home state has enjoyed far more stable rates after tort reforms eased litigation costs on insurers.
Previous research by the Insurance Research Council (IRC) – like Triple-I, an affiliate of the Institutes – showed that most consumers perceive the link between attorney advertising and higher insurance costs. Crawford’s Verma, however, emphasized that this awareness does not necessarily translate into consumers understanding their own agency.
“It’s easier for homeowners to understand how the weather impacts potential losses and the fact that weather patterns have changed,” Verma said. “But when it comes to [legal system abuse], I don’t think that connection is as well understood.”
Reflecting on a record high in nuclear verdicts last year, Rivera suggested insurers must reconfigure how they communicate legal system abuse to consumers.
“Where are those hospital professional liability verdicts going to go?” he said. “They’re going to go back into the cost of health care at the end of the day.”
Leading the AI charge
Maintaining consumer centricity while implementing or experimenting with technological innovations – especially generative AI – was a unifying objective for all the panelists.
“We look at AI as an enabler,” Brown said, “so we can put teammates in a position to spend more time with customers, which is the most important thing.”
For Tokio Marine’s Rivera, AI “ultimately helps all of our insureds” by boosting operational efficiency while reducing operational costs, as well as facilitating more proactive risk management than ever before. A growing percentage of insurance executives appear to agree, as generative AI models continue to expedite data processing across the insurance value chain, reshaping underwriting, pricing, claims, and customer service.
Such efficiency, paired with the potential for improved decision-making, is crucial “in our dramatically changing environment,” Marchioni stressed.
“We have thousands of claims every day,” he said. “Thinking about lawsuit abuse as a backdrop – a claims adjuster, every day, has to make decisions regarding, ‘Do I settle this claim based on injuries or venue? What’s the value of the injury and of the claim? Who’s the plaintiffs’ attorney?’ These tools give more refined information so your knowledge workers can make better, more timely decisions.”
Generative AI fails, however, when base datasets are insufficient, outdated, or inaccurate, Brown pointed out. Training AI models uncritically can lead to outputs containing false and/or nonsensical information, commonly known as “hallucinations”.
At their current capacity, at least, AI models cannot draw the kinds of salient conclusions that adjustors and underwriters can, meaning AI could “change the way we work, but it’s not going to replace the jobs,” Verma said.
Though they do not currently exist in the United States at the federal level, AI regulations have already been introduced in some states, following a comprehensive AI Act enacted last year in Europe. With more legislation on the horizon, insurers must help lead these conversations to ensure that AI regulations suit the complex needs of insurance, without hindering the industry’s commitments to equity and security.
A 2024 report by Triple-I and SAS, a global leader in data and AI, centers the insurance industry’s role in guiding conversations around ethical AI implementation on a global, multi-sector scale, given insurers’ unique expertise in analyzing and preserving data integrity.
Learn More:
Insurance Affordability, Availability Demand Collaboration, Innovation
Executive Exchange: Insuring AI-Related Risks
Tariff Uncertainty May Strain Insurance Markets, Challenge Affordability
Reining in Third-Party Litigation Funding Gains Traction Nationwide
Claims Volume Up 36% in 2024; Climate, Costs, Litigation Drive Trend
Personal Cyber Risk Is Up; Why Isn’t Adoption of Personal Cyber Coverage?
U.S. Cyber Claims Surge While Global Rates Decline: Chubb
FBI: Elder Fraud Up; Bolsters Case for Personal Cyber Insurance
Triple-I Issues Brief: Cyber Insurance (Members Only)
Triple-I Issues Brief: Legal System Abuse (Members Only)