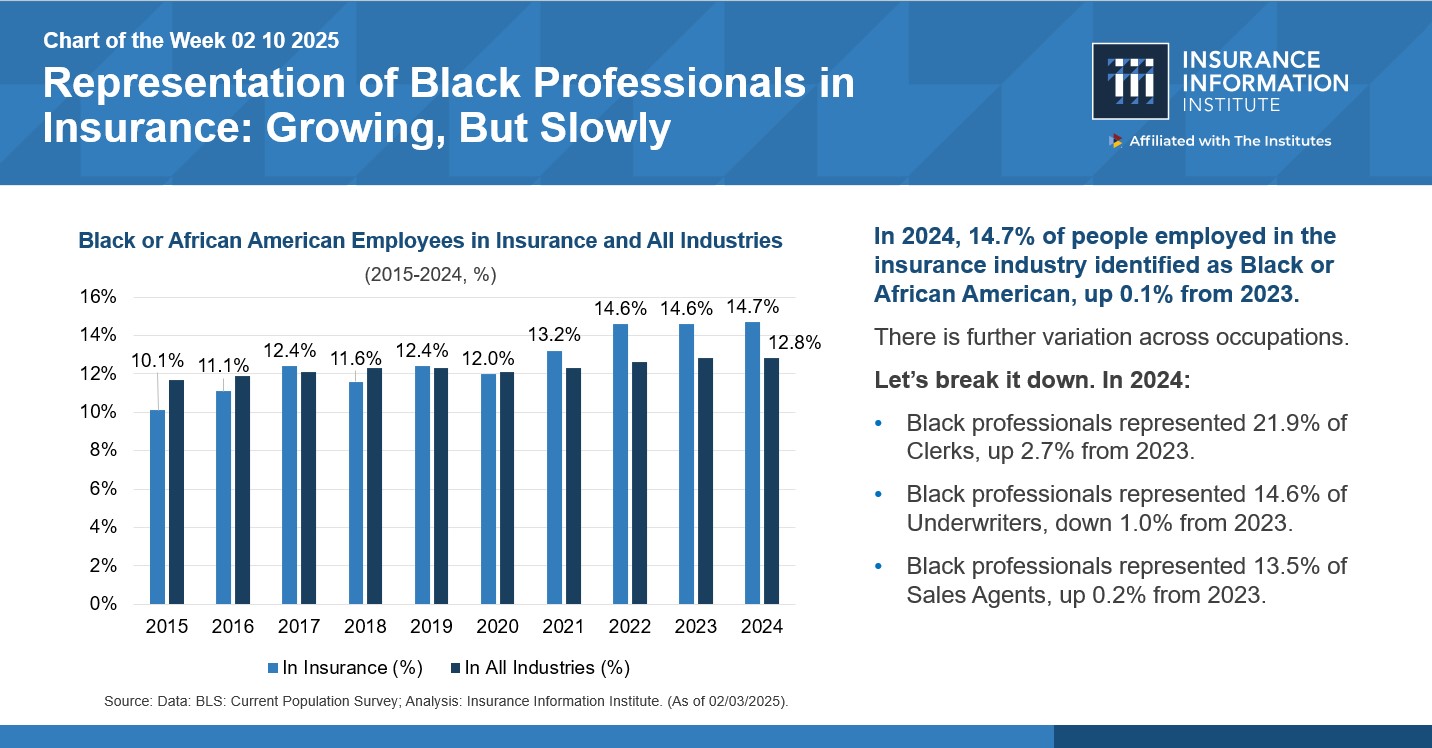
Recent tariffs issued by U.S. President Donald Trump are on track to increase the price of parts and materials used in repairing and restoring property after an insurable event. Analysts and economists, predict these price hikes will lead to higher claim payouts for P&C insurers and, ultimately, higher premiums for policyholders.
After making several announcements since early March 2025, on April 2, President Trump signed an executive order imposing a minimum 10 percent tariff on all U.S. imports, with higher levies on imports from 57 specific trading partners. A general tariff rate became effective on April 5, while tariffs on imports from the targeted nations, ranging from 11 to 50 percent, took effect on April 9. A 25 percent tariff applies to all steel and aluminum imports and cars. President Trump says he might consider a one-month exemption to the auto industry, but as of this writing, no changes have been issued.
Generally, tariffs can bring in revenue for the issuing government but lower the operating margin for impacted domestic businesses. Inventory and supply chain managers may attempt to stockpile in advance of the new rates becoming effective, which in turn can spike demand and quickly spike prices for sought-after items. Eventually, these cost hikes get passed on to consumers.
Nonetheless, to ride out the situation, inventory and supply chain managers need a fundamental level of predictability regarding what the levies will cover, what the rates are, and when these rates go into effect. The timing and scope of President Trump’s tariff policies have been challenging to nail down, including for many goods particularly relevant to construction and auto manufacturing. For example, his initially declared rates for major trading partners – Canada, Mexico, the European Union, and China – have fluctuated as these nations announced reciprocal tariffs, and those levies, in turn, were met with higher US rates.
Then, on April 9, President Trump declared a 90-day pause on tariffs. This change was actually not a true pause but a reduction of previous rates for several countries to 10 percent, except for China. The White House has declared on April 10 that the previously announced 125 percent rate against goods from China is actually now 145 percent.
According to S&P, the levy on auto industry imports has been comparatively less dynamic as, despite confusing announcements from the White House, there has been no change to President Trump’s 25 percent rate declared on March 26, “which applies to all light-vehicle imports, regardless of country. The 25 percent tariff includes auto parts as well as completely built up (CBU) vehicles. The CBU autos tariff went into effect on April 3, 2025, while the auto parts portion is due to come into effect on May 3, 2025.”
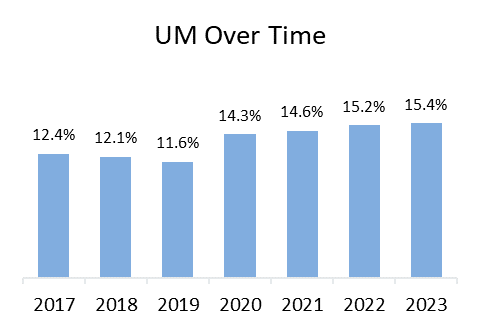
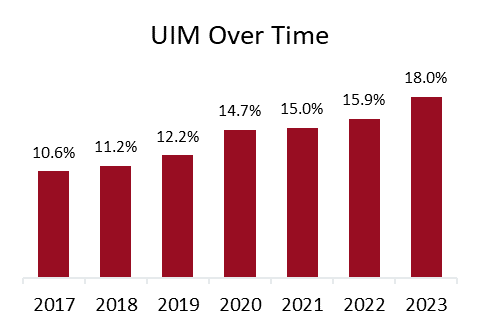
As insurers grapple with risk management and inflationary pressures, other challenges posed by the tariffs can include issues for policyholders, specifically coverage affordability and availability. One downstream side effect may be the increased risk of expanding the protection gap – uninsurance and underinsurance (UM/UIM) due to higher premiums and higher valuations that can come into play when materials costs rise. Across the fifty states and the District of Columbia, one in three drivers (33.4 percent) were either uninsured or underinsured in 2023, according to a recent report, Uninsured and Underinsured Motorists: 2017–2023, by the Insurance Research Council (IRC), affiliated with The Institutes.
Our Chief Economist and Data Scientist, Dr. Michel Léonard, shares his analysis of how the tariffs may impact the P&C Insurance industry.
“There’s no crystal ball”, say Dr. Léonard, “but prudent risk underwriting and risk management suggests the use of scenarios and increased price ranges for different tariff levels, the more precise impact of which can be updated based on actual price increases for individual prices.”
Dr. Léonard outlines three types of P&C replacement cost scenarios given different tariff ranges:
1) For single-digit tariffs, while inventories last, higher prices below that tariff’s rate;
2) for single-digit tariffs on goods still economically viable post-tariffs, higher prices up to the tariff’s rate; and
3) for single and double-digit tariffs on goods no longer economically viable, a multiple of the pre-tariff price for tariff-evading goods.
His presentation, Tariffs and Insurance: Economic Insights can be previewed, but the full version is currently available exclusively to Triple-I members.
Triple-I remains committed to keeping abreast of these and other developments crucial to the insurance industry’s future. For more information, we invite you to stay tuned to our blog and join us at JIF 2025.