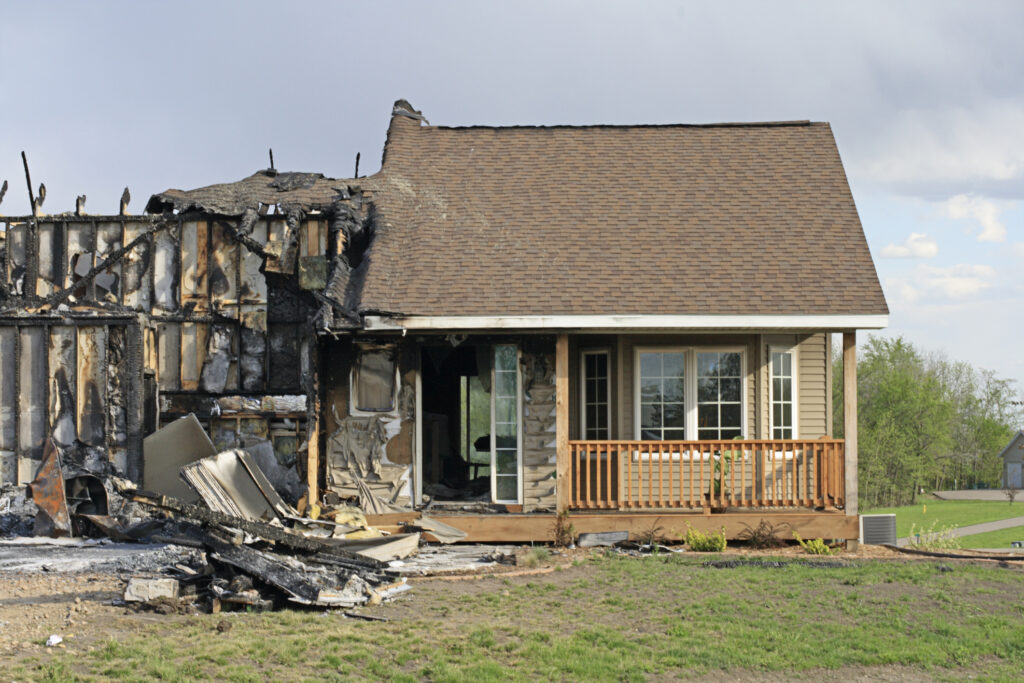
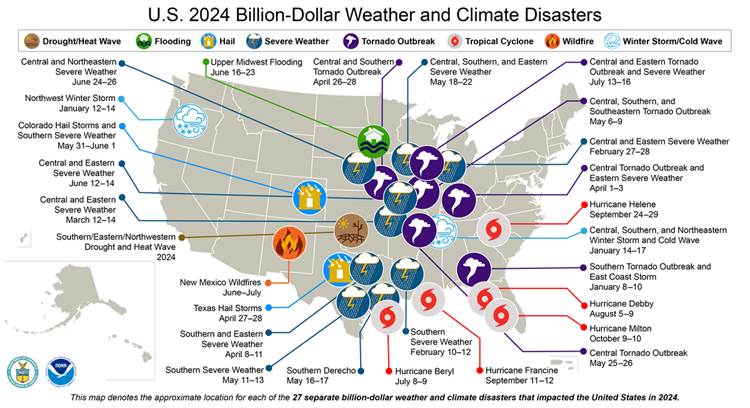
A recent paper published in Nature that analyzes five major California wildfires confirms what insurers, fire scientists, and risk modelers have long asserted: Defensible space and home hardening help mitigate wildfire risk and improve resilience.
The study found that clearing vegetation and flammable materials within 1.5 meters of a structure — an area known as “Zone 0” — is one of the most effective actions a homeowner can take. When this is paired with home-hardening features like non-combustible siding, enclosed eaves, and vent screens, the results are staggering: predicted losses dropped by as much as 48 percent, according to the study.
Homes built after 1997, when California adopted stricter building codes, consistently outperformed older structures. These newer homes incorporated fire-resistant materials and design features that significantly improved survival rates.
From an insurance perspective, such steps – by leading to reduced losses and fewer, less-costly claims – can alleviate some of the upward pressure on premium rates in areas at higher risk for wildfire. In the long term, they can improve insurance affordability and availability in fire-vulnerable geographies.
Wildfire risk is strongly conditioned by geographic considerations that vary widely across and within states. A recent paper by Triple-I and Guidewire – a provider of software solutions to the insurance industry – used case studies from three California areas with very different geographic and demographic characteristics to go deeper into how such tools can be used to identify properties with attractive risk properties, despite their location in wildfire-prone areas. The use of such data-driven analysis can help insurers identify less risky properties within higher-risk geographies.
The study in Nature examined five major fires from recent history in the wildland-urban interface (WUI) – Tubbs (2017), Thomas (2017), Camp (2018), Kincade (2019), and Glass (2020) – using machine learning to analyze on-the-ground post-fire data collection, remotely sensed data, and fire reconstruction modeling to assess patterns of loss and mitigation effectiveness.
Using a tool called an XGBoost classifier, the study found that “structure survivability can be predicted to 82 percent.” The study reported that “spacing between structures is a critical factor influencing fire risk…while fire exposure, the ignition resistance (hardening) of structures, and clearing around structures (defensible space) work in combination” to mitigate that risk.
“With the science-based information from this report, we can reduce risk and make our communities safer from wildfire,” said Janet Ruiz, Triple-I’s California-based director of strategic communication. Accuracy of 82 percent on predictability of structures burning is a major improvement, and mitigation is the key.”
Coordinated community-wide strategies like vegetation management, building code enforcement, and distance between structures are essential. Triple-I and its members and partners are working to inform, educate, and drive behavioral change to reduce risk and build resilience.
Learn More:
Triple-I Brief Highlights Wildfire Risk Complexity
P&C Insurance Achieves Best Results Since 2013; Wildfire Losses, Tariffs Threaten 2025 Prospects
Data Granularity Key to Finding Less Risky Parcels in Wildfire Areas
California Finalizes Updated Modeling Rules, Clarifies Applicability Beyond Wildfire