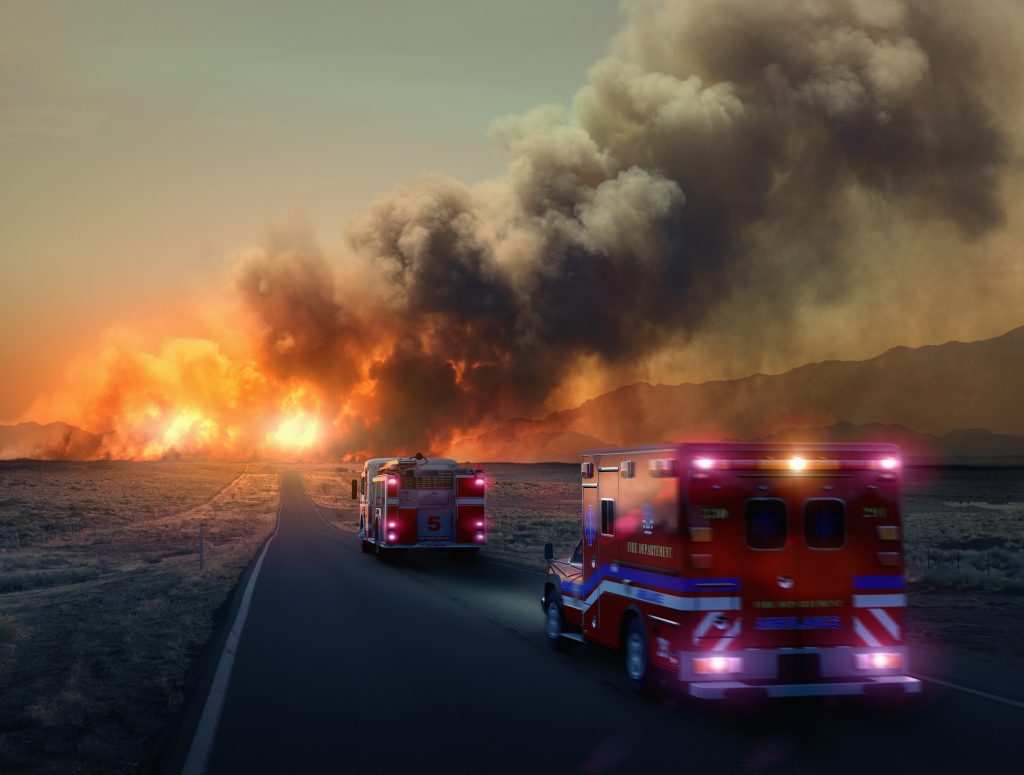
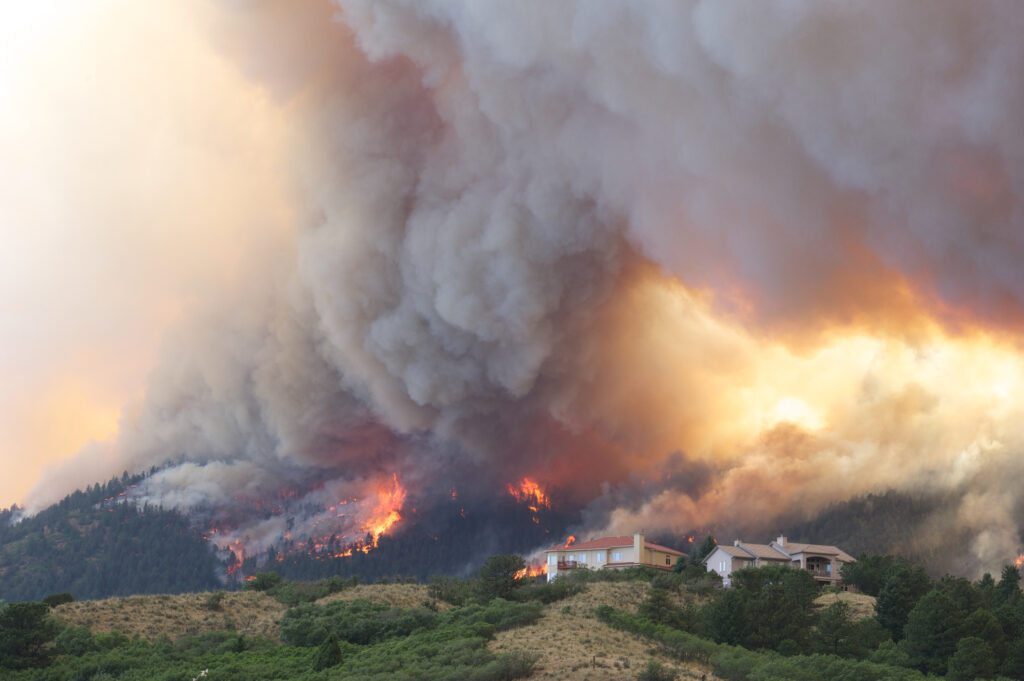
Even as the Smokehouse Creek Fire – the largest wildfire ever to burn across Texas – was declared “nearly contained” this week, the Texas A&M Service warned that conditions are such that the remaining blazes could spread and even more might break out.
“Today, the fire environment will support the potential for multiple, high impact, large wildfires that are highly resistant to control” in the Texas Panhandle, the service said.
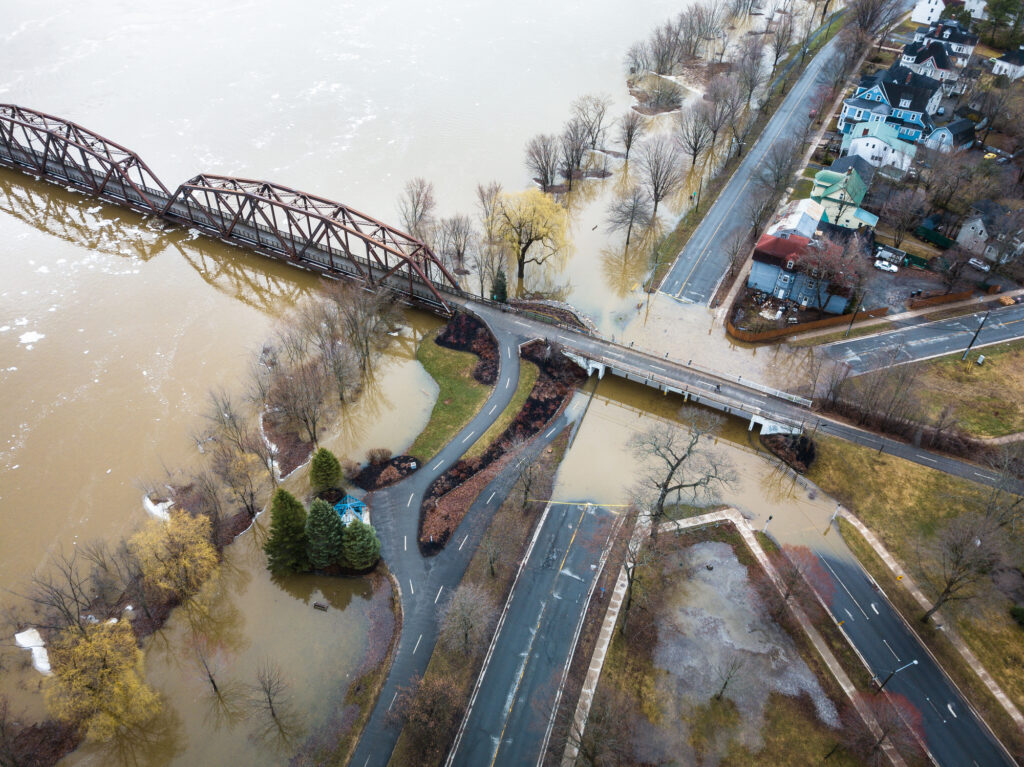
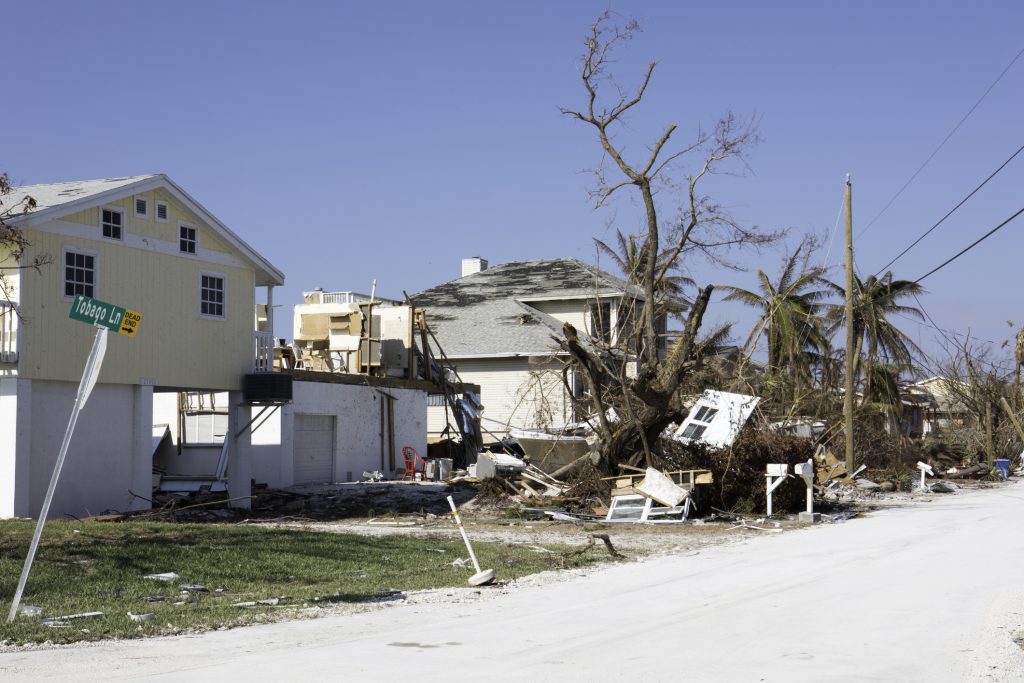
This year’s historic Texas fires – like the state’s 2021 anomalous winter storms, California’s recent flooding after years of drought, and a surge in insured losses due to severe convective storms across the United States – underscore the variability of climate-related perils and the need for insurers to be able to adapt their underwriting and pricing to reflect this dynamic environment. It also highlights the importance of using advanced data capabilities to help risk managers better understand the sources and behaviors of these events in order to predict and prevent losses.
For example, Whisker Labs – a company whose advanced sensor network helps monitor home fire perils, as well as tracking faults in the U.S. power grid – recorded about 50 such faults in Texas ahead of the Smokehouse Creek fires.
Bob Marshall, Whisker Labs founder and chief executive, told the Wall Street Journal that evidence suggests Xcel Energy’s equipment was not durable enough to withstand the kind of extreme weather the nation and world increasingly face. Xcel – a major utility with operations in Texas and other states — has acknowledged that its power lines and equipment “appear to have been involved in an ignition of the Smokehouse Creek fire.”
“We know from many recent wildfires that the consequences of poor grid resilience can be catastrophic,” said Marshall, noting that his company’s sensor network recorded similar malfunctions in Maui before last year’s deadly blaze that ripped across the town of Lahaina.
Role of government
Government has a critical role to play in addressing the risk crisis. Modernizing building and land-use codes; revising statutes that facilitate fraud and legal system abuse that drive up claim costs; investing in infrastructure to reduce costly damage related to storms – these and other avenues exist for state and federal government to aid disaster mitigation and resilience.
Too often, however, the public discussion frames the current situation as an “insurance crisis” – confusing cause with effect. Legislators, spurred by calls from their constituents for lower premiums, often propose measures that would tend to worsen the problem because they fail to reflect the importance of accurately valuing risk when pricing coverage.
The federal “reinsurance” proposal put forth in January by U.S. Rep. Adam Schiff of California is a case in point. If enacted, it would dismantle the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) and create a “catastrophic property loss reinsurance program” that, among other things, would set coverage thresholds and dictate rating factors based on input from a board in which the insurance industry is only nominally represented.
U.S. Rep. Maxine Waters (also of California) has proposed a Wildfire Insurance Coverage Study Act to research issues around insurance availability and affordability in wildfire-prone communities. During House Financial Services Committee deliberations, Waters compared current challenges in these communities to conditions related to flood risk that led to the establishment of NFIP in 1968. She said there is a precedent for the federal government to step in when there is a “private market failure.”
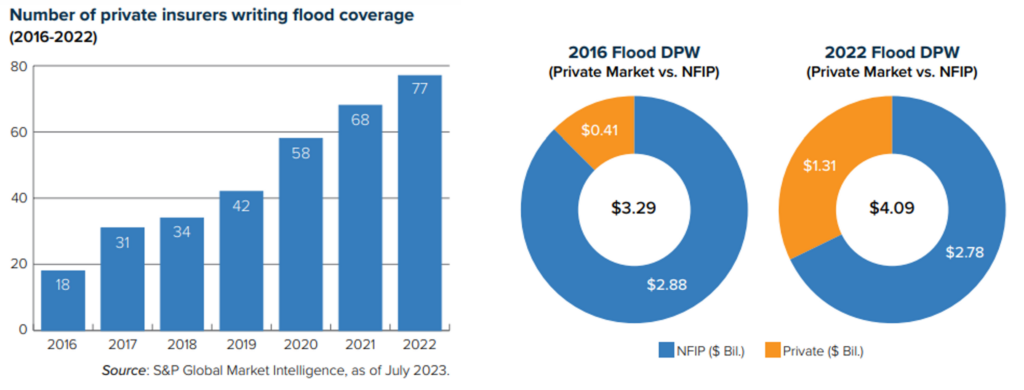
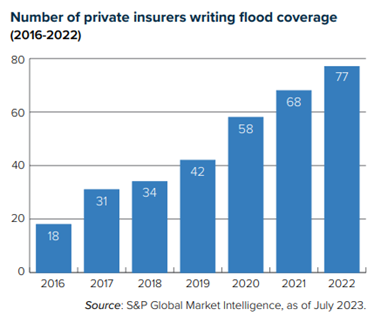
However, flood risk in 1968 and wildfire risk in 2024 could not be more different. Before FEMA established the NFIP, private insurers were generally unwilling to underwrite flood risk because the peril was considered too unpredictable. The rise of sophisticated computer modeling has since given private insurers much greater confidence covering flood (see chart).
In California, some insurers have begun rethinking their appetite for writing homeowners insurance – not because wildfire losses make properties in the state uninsurable but because policy and regulatory decisions made over 30 years ago have made it hard to write the coverage profitably. Specifically, Proposition 103 and its regulatory implementation have blocked the use of modeling to inform underwriting and pricing and restricted insurers’ ability to incorporate reinsurance costs into their premium pricing.
California’s Insurance Commissioner Ricardo Lara last year announced a Sustainable Insurance Strategy for the state that includes allowing insurers to use forward-looking risk models that prioritize wildfire safety and mitigation and include reinsurance costs into their pricing. It is reasonable to expect that Lara’s modernization plan will lead to insurers increasing their business in the state.
It’s understandable that California legislators are eager to act on climate risk, given their long history with drought, fire, landslides and more recent experience with flooding due to “atmospheric rivers.” But it’s important that any such measures be well thought out and not exacerbate existing problems.
Partners in resilience
Insurers have been addressing climate-related risks for decades, using advanced data and analytical tools to inform underwriting and pricing to ensure sufficient funds exist to pay claims. They also have a natural stake in predicting and preventing losses, rather than just continuing to assess and pay for mounting claims.
As such, they are ideal partners for businesses, communities, governments, and nonprofits – anyone with a stake in climate risk and resilience. Triple-I is engaged in numerous projects aimed at uniting diverse parties in this effort. If you represent an organization that is working to address the risk crisis and your efforts would benefit from involvement with the insurance industry, we’d love to hear from you. Please contact us with a brief description of your work and how the insurance industry might help.
Learn More:
Triple-I “State of the Risk” Issues Brief: Wildfire
Triple-I “State of the Risk” Issues Brief: Flood
Triple-I “Trends and Insights” Issues Brief: California’s Risk Crisis
Triple-I “Trends and Insights” Issues Brief: Risk-Based Pricing of Insurance
Stemming a Rising Tide: How Insurers Can Close the Flood Protection Gap