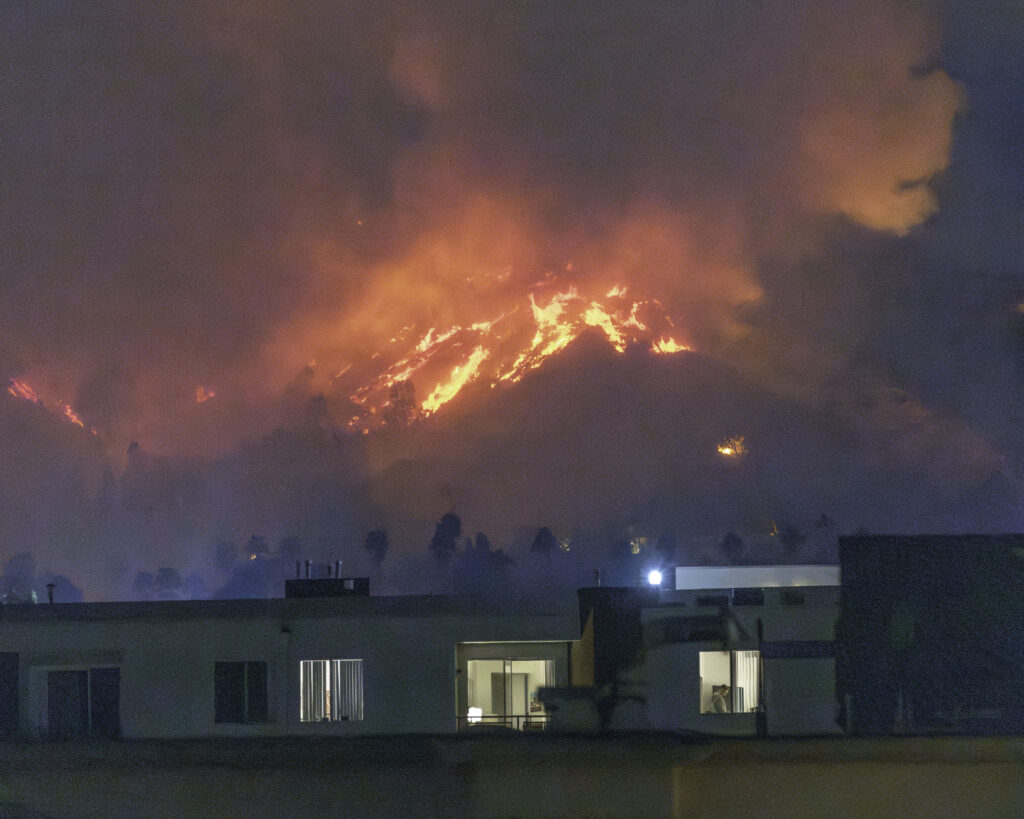
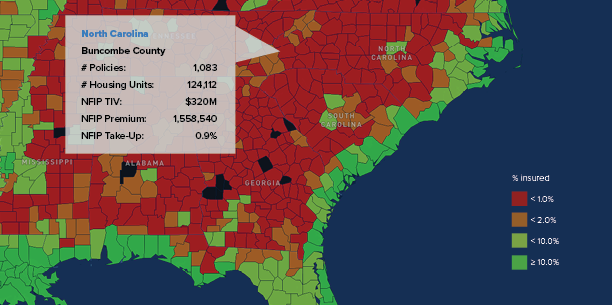
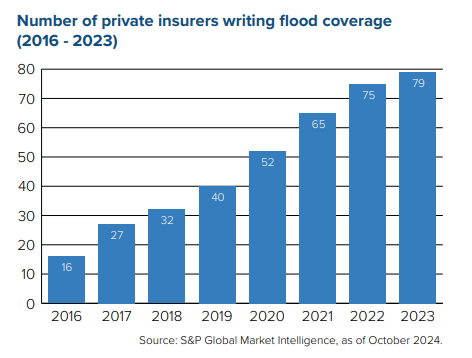
As high-severity natural catastrophes – wildfires, floods, hurricanes, and others – become more frequent and more people move into riskier locales, insurance affordability and availability have become a challenge in many states.
Insurers underwrite and price coverage based on the risks they’re assuming, and rising premiums in these states have pushed more homeowners into residual market mechanisms, such as state-backed insurance pools or agencies. Reliance on these funds – which often provide more limited coverage at higher costs – is not sustainable in the long term.
To ensure market stability and continued insurance availability and affordability, insurers must leverage more granular and dynamic risk models that account for real-time environmental conditions, mitigation measures, and property-specific characteristics. A new paper by Triple-I and Guidewire – a provider of software solutions to the insurance industry – uses case studies from three California areas with very different geographic and demographic characteristics to show how such tools can be used to identify properties with attractive risk properties, despite their location in wildfire-prone areas.
California’s risk profile
In addition to its particular risk characteristics, California’s insurance challenge is exacerbated by a 1988 measure – Proposition 103 – that has constrained insurers’ ability to profitably insure property in the state. In a dynamically evolving risk environment that includes earthquakes, drought, wildfire, landslides, and damaging floods, regulatory interpretation of Proposition 103 has made it hard for some insurers to offer coverage in the state.
In some cases, this has led to insurers limiting or reducing their business in the state. With fewer private insurance options available, more Californians are resorting to the state’s FAIR Plan, which offers less coverage for a higher premium. For many, this “insurer of last resort” has become the insurer of first resort. This isn’t a tenable situation for the state or its policyholders. California’s insurance availability/affordability challenges will require a multi-pronged approach, and underlying every component is the need for granular, high-quality, reliable data.
Modeling based on granular data
Guidewire’s analysis, based on its HazardHub Wildfire Score, has shown that wildfire mitigation and home hardening can reduce wildfire damage by as much as 70 percent. But identifying less risky lots in such areas is no easy task.
“Every property being assessed for wildfire risk is unique,” the report says. “Therefore, it’s important to subject as many relevant variables as possible to analysis. For example, proximity of structures to fuel is important – but, to be more predictive, it helps to know more: What kind of fuel? Is there potential for a wind-driven event? Is the property on a hill? If so, is it north-facing?”
Guidewire’s model includes standard variables, such as slope, aspect, wildfire history, wind, and the amount of nearby vegetation. It also includes differentiators like vegetation type and fire-suppression success rate.
“The traditional approach to wildfire risk assessment has left many Californians without access to affordable property insurance coverage,” said Triple-I Chief Insurance Officer Dale Porfilio. “Our research shows that with more detailed, property-level analysis, insurers can confidently offer coverage in areas previously deemed too risky.”
Important moves by California
California has taken steps to address regulatory obstacles to fair, actuarially sound insurance underwriting and pricing – most notably, the state’s Sustainable Insurance Strategy, an ambitious plan released by Insurance Commissioner Ricardo Lara in 2023 plan aimed at safeguarding the health of the insurance market while ensuring long-term sustainability. A key component of the plan is a requirement that insurers writing homeowners coverage in the state write no less than 85 percent of their statewide market share in areas identified by the commissioner as “under-marketed.”
Tightly focused, data-driven analysis using tools like the HazardHub Wildfire Score, can go a long way toward helping insurers meet those requirements by identifying less risky parcels in undermarketed areas.
“The Triple-I analysis highlights how next-generation tools and data can uncover lower-risk properties – even in high-risk areas – empowering insurers to expand coverage confidently and responsibly,” said Leo Tenenblat, Senior Vice President and General Manager, Data and Analytics at Guidewire.
Learn More:
Despite Progress, California Insurance Market Faces Headwinds
California Insurance Market at a Critical Juncture
California Finalizes Updated Modeling Rules, Clarifies Applicability Beyond Wildfire
California Risk/Regulatory Environment Highlights Role of Risk-Based Pricing