By Lewis Nibbelin, Contributing Writer, Triple-I
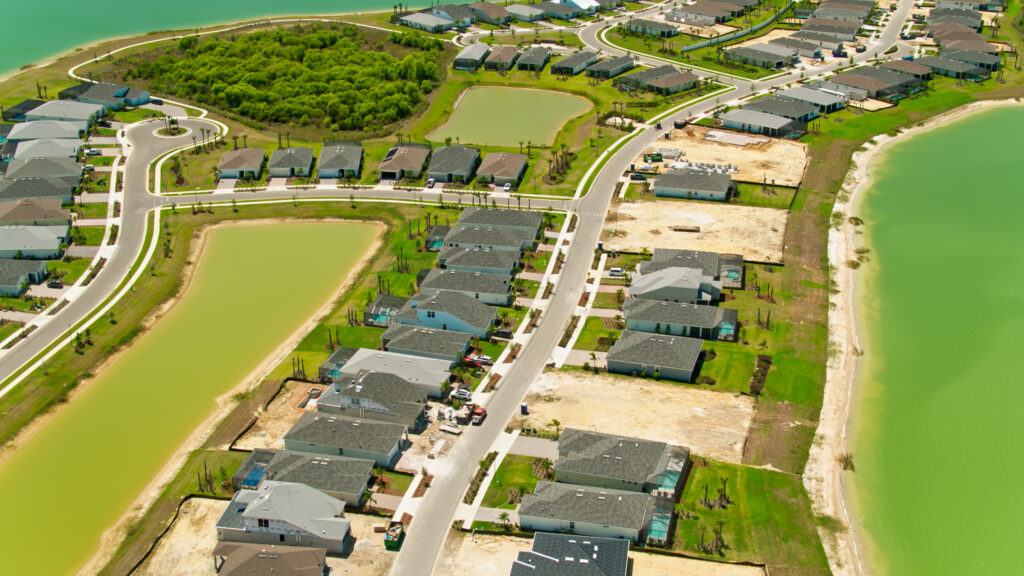
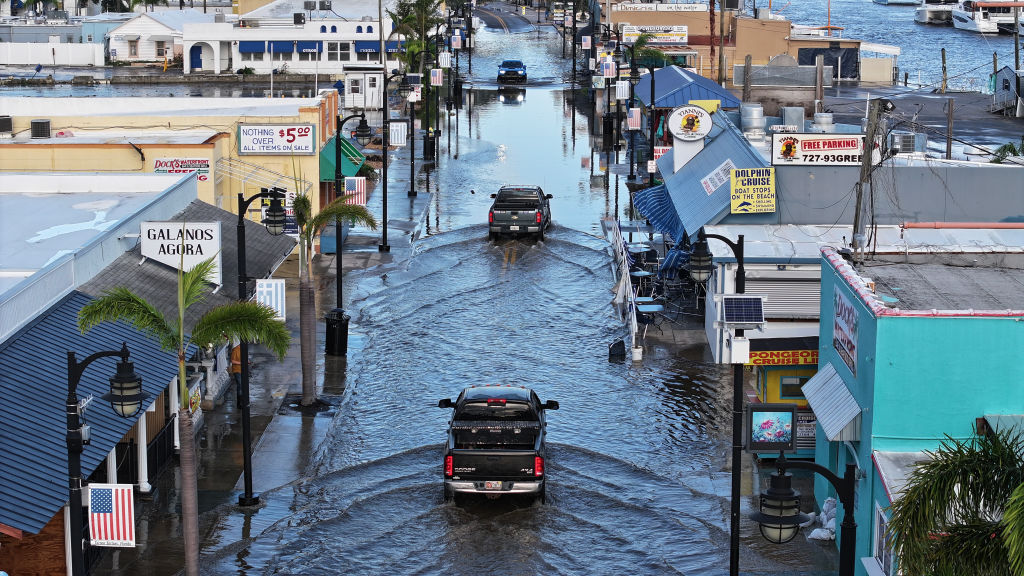
Babcock Ranch – a small community in southwestern Florida dubbed “The Hometown of Tomorrow” – made headlines for sheltering thousands of evacuees and never losing power during Hurricane Milton, which devastated numerous neighboring cities and left more than three million people without power.
Hunters Point, a subdivision on Florida’s Gulf Coast, remained similarly unscathed during both Hurricanes Helene and Milton. Though the development is only two years old, it’s already been through four major hurricanes. Its homes were designed with an elevation high enough to avoid severe flooding and materials that make them as sturdy as possible in high winds. When the power goes out, each home turns to its own solar panels and battery system.
For residents of both communities, this news comes as no surprise; their flood-resistant infrastructure and solar panel power systems have helped them survive several storms and hurricanes with only minor damages, demonstrating the utility of disaster resilience planning.
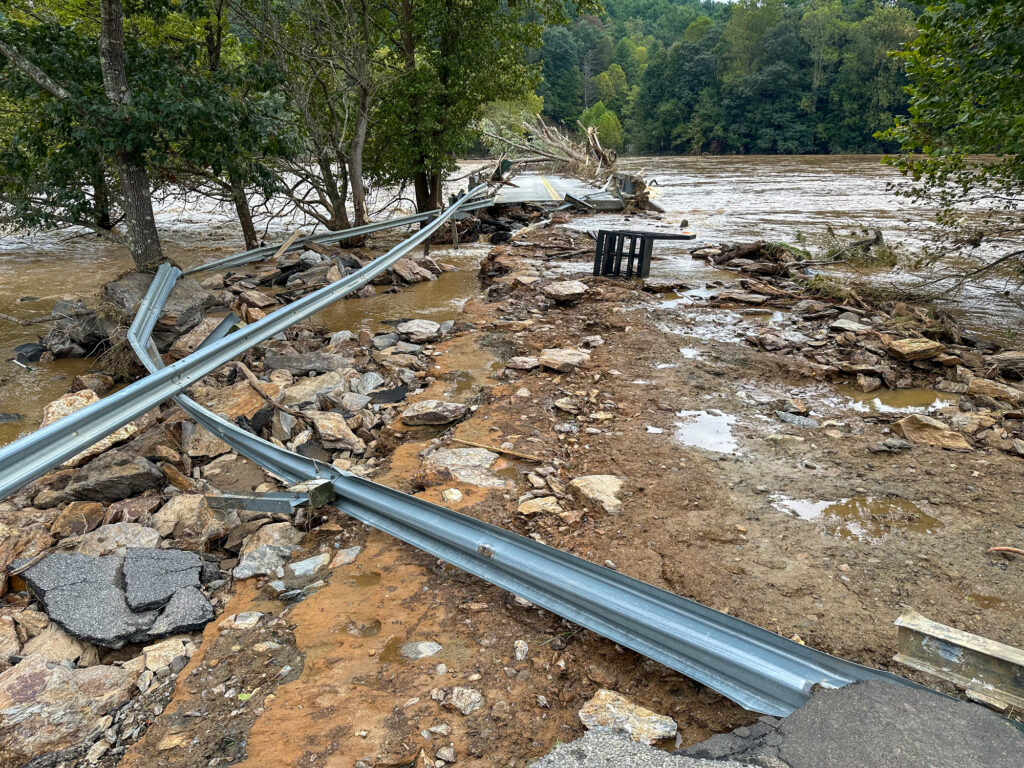
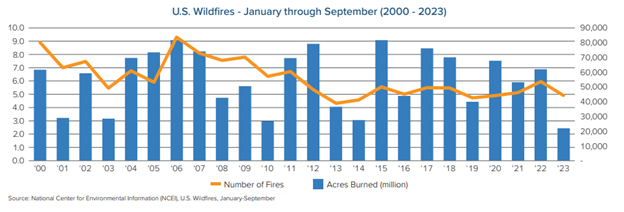
Such planning is expensive to implement. Homes in either community can run for over a million dollars. But, as the combined costs of Hurricanes Helene and Milton rise to the tens of billions, it’s hard to overstate the long-term benefits. Every dollar invested in disaster resilience could save 13 in property damage, remediation, and economic impact costs, suggesting risk mitigation and recovery strategies will become even more essential as natural catastrophe severity increases.
Incentivizing investment
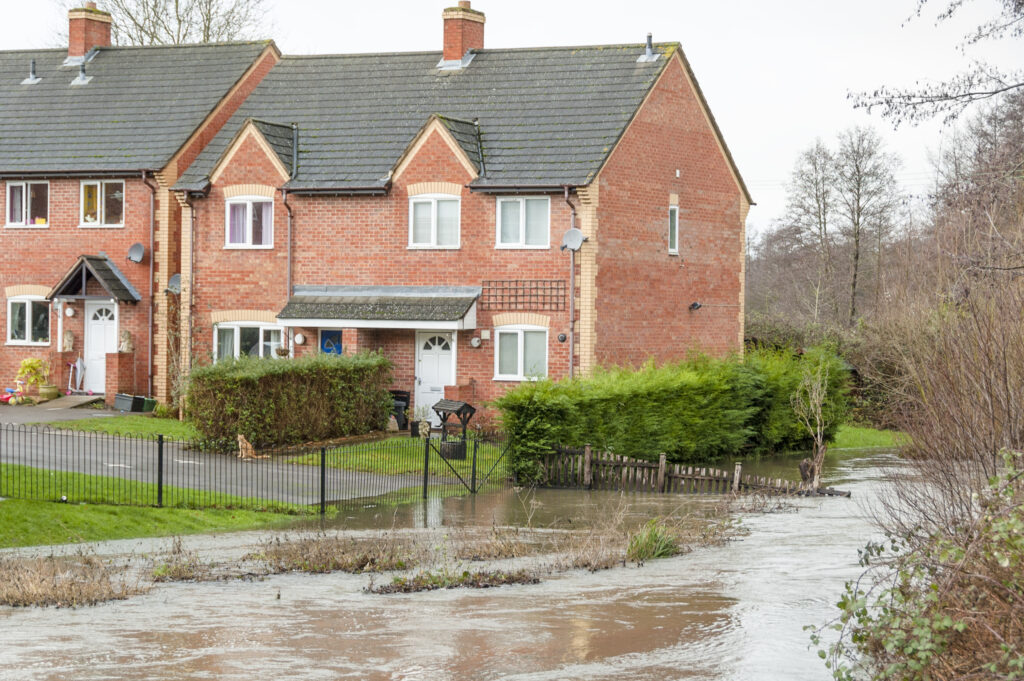
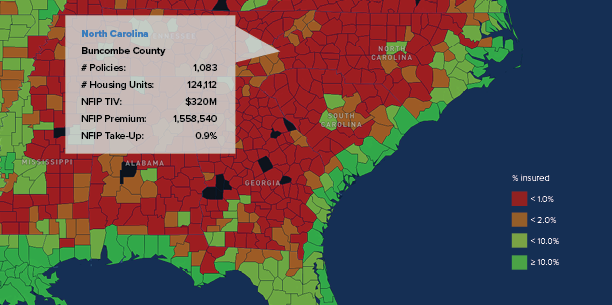
The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) Community Rating System (CRS) – a voluntary program that rewards homeowners with reduced premiums when their communities invest in floodplain management practices that exceed NFIP minimum standards – aims to encourage resilience. Class 1 is the program’s highest rating, qualifying residents for a 45 percent reduction in their premiums. Of the nearly 23,000 participating NFIP communities, only 1,500 participate in the CRS. Of those 1,500, only two – Tulsa, Okla., and Roseville, Calif. – have achieved the highest rating.
High ratings are difficult to secure and maintain. Homeowners in Lee County, which borders Babcock Ranch, nearly lost their discounts earlier this year due to improper post-Hurricane Ian monitoring and documentation within flood hazard areas.
Discounts in lower-rated jurisdictions, however, still equate to large premium reductions. Miami-Dade County, Fla., for instance, earned a Class 3 rating after extensive stormwater infrastructure upgrades, saving the community an estimated $12 million annually. Residents sustained minimized flooding from Hurricane Milton under these improvements, further justifying their cost.
Local mitigation efforts offer targeted resilience solutions and resources to alleviate community risks. The insurance industry-funded Strengthen Alabama Homes provides homeowners grants to retrofit their houses along voluntary standards for constructing buildings resistant to severe weather. Completed retrofits reduce post-disaster claims and qualify grantees for substantial insurance premium discounts, prompting flood-prone Louisiana to replicate the program.
Other nature-based planning exploits local flora as a source of natural hazard protection. Previous studies support conserving natural wetlands and mangroves to impede the rate and flow of flooding, leading many communities – including Babcock Ranch, which is 90 percent wetlands – to invest in green infrastructure. Reforestation and wetland restoration projects undertaken by the Milwaukee Metropolitan Sewerage District (MMSD) also promise to store or capture millions of gallons of storm and flood water, enabling risk management alongside improved quality of life for citizens.
Most resilience projects are impossible to fund or operate without stakeholder partnerships and advanced data and analytics. Insurers, who have long assessed and measured catastrophe risk utilizing cutting-edge data tools, are uniquely positioned to confront these evolving risks and present a framework for successful preemptive mitigation.
Learn More:
Hurricane Helene Highlights Inland Flood Protection Gap
Removing Incentives for Development From High-Risk Areas Boosts Flood Resilience
Executive Exchange: Using Advanced Tools to Drill Into Flood Risk
Accurately Writing Flood Coverage Hinges on Diverse Data Sources
Legal Reforms Boost Florida Insurance Market; Premium Relief Will Require More Time
Lee County, Fla., Towns Could Lose NFIP Flood Insurance Discounts