The Insurance Information Institute (Triple-I) has released its latest issues brief, Legal System Abuse and Attorney Advertising for Mass Litigation: State of the Risk, which discusses how mass torts, specifically Multidistrict Litigation, and aggressive attorney advertising can in combination fuel the risk of legal system abuse.
Advertising is one of the most common methods companies use to sell their products and services and influence public perceptions. While the issue brief doesn’t argue that general advertising or filing for due process is problematic, it does offer a risk management-based lens for viewing how aggressive attorney advertising campaigns can fuel costs associated with settling claims.
Key Findings
- Legal service providers spent $2.5 billion on 26.9 million ads across the United States.
- Research suggests that legal advertising increases the number of plaintiffs in multidistrict litigation (MDL), which are large lawsuits consisting of multiple civil cases involving one or more common questions of fact but pending in different districts.
- Product liability cases, which accounted for 38 percent of pending MDLs as of August 2023, emerged as the single largest category of MDLs, while other case types have decreased from 2012 to 2022.
- The third-party litigation funding market, with an estimated size of $16 billion, is a likely resource for advertising budgets for mass torts; however, 12 states and two jurisdictions have enacted or are considering disclosure requirements.
Ads for legal services and lawsuits saturate all channels of communication – public billboards, radio and television broadcasts, and social media – dangling the lure of a financial windfall. Legal services marketing isn’t uniquely used for mass litigation cases. Nonetheless, it is overall geared to recruit as many lawsuit filers as possible. Therefore, aggressive advertising for legal services introduces the risk of fueling higher claim costs via problematic litigation.
These advertisements often employ an exaggerated sense of urgency, urging the target audience to take immediate legal action without considering alternative options for resolution. These ads may also often overpromise results by implying guaranteed windfalls (i.e., “We’ll get you your money’’), creating unrealistic expectations for plaintiffs and, thus, potentially impacting the time to settle. Additionally, when ads mention a particular product or brand, attorneys communicate plaintiff-biased information to potential jurors. In essence, a juror may recall seeing a flood of advertisements about the product and think, “Where there’s smoke, there must be fire.”
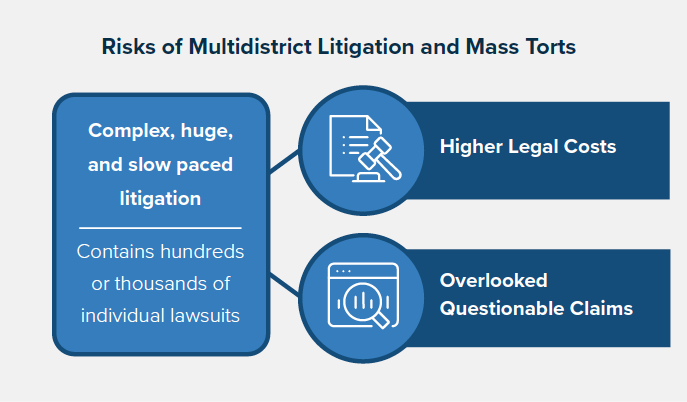
The brief focuses on MDLs because these are complex, huge, and slow-paced cases that may sometimes involve hundreds, even thousands of individual lawsuits. Therefore, these cases inherently carry the risk of driving up legal costs. Also, the large number of plaintiffs introduces the risk that questionable claims might slip into the lawsuit. For example, a particular product may have indeed caused harm to some, but not all, of the plaintiffs who used it.
Pummeling the world with ads can be expensive. Enter the third-party litigation funding (TPLF) market, which, despite tighter capital controls in recent years, grew to $16 billion in 2024, up from $15.2 billion in 2023. TPLF offers discretionary funding to the litigation industry, which can, in turn, use the money to fuel more lawsuits seeking large settlements — a boon for the firms and the funder. The brief outlines how several states and jurisdictions are moving to create transparency around TPLF involvement.
Practices that foster unnecessary or drawn-out litigation are among several hard-to-measure forces that can shift loss ratios for insurers and disrupt forecasts, making cost management more challenging. Ultimately, the cost is passed on to consumers, adversely impacting coverage affordability and availability. Triple-I is committed to advancing conversations with business leaders, government regulators, consumers, and other stakeholders to attack the risk crisis and chart a path forward.
Read the issue brief to find out more about how attorney advertising can contribute to legal system abuse. To join the discussion, register for JIF 2025. Follow our blog to learn more about trends in insurance affordability and availability across the property/casualty market.