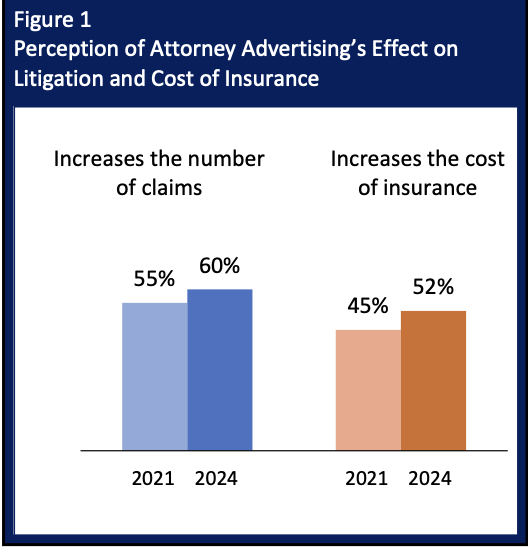
According to a new survey conducted by the Insurance Research Council (IRC), most consumers believe attorney advertising increases the number of claims and lawsuits and the cost of auto insurance.
The report, Public Opinions on Attorney Involvement in Claims, analyzes consumer opinions on attorney involvement in insurance claims and expands prior research. Overall, 60 percent of 2000 respondents in this latest nationwide online survey from IRC said that attorney advertising increases the number of claims, and 52 percent said that advertising increases the cost of insurance. Most respondents (89 percent) reported seeing attorney advertising in the past year, and about half reported seeing an increase in the amount of attorney advertising.
The IRC endeavored to gauge perceptions of attorney advertising and its impact on the cost of insurance, consumer awareness and understanding of litigation financing practices, and decisions about consulting attorneys about auto insurance claims. The main lines of inquiry in the survey revolved around:
- How has the public experienced attorney advertising, and what do they think of the impact?
- Are they aware of litigation financing, and after being given a description, what do they think of it?
- Would they be more likely to hire an attorney to help settle an insurance claim or to settle directly with an insurer?
- What was their previous history with auto insurance claims and their experience with consulting a lawyer to help settle an injury claim?
Results indicate that consumers are exposed to more attorney advertising across most mediums – particularly in outdoor ads, with auto accident advertisements being the most prevalent medium – compared to three years ago. While billboard advertising has experienced the most growth over the past three years, TV is the most recalled medium, with 65 percent of respondents recalling seeing TV ads in the past year.
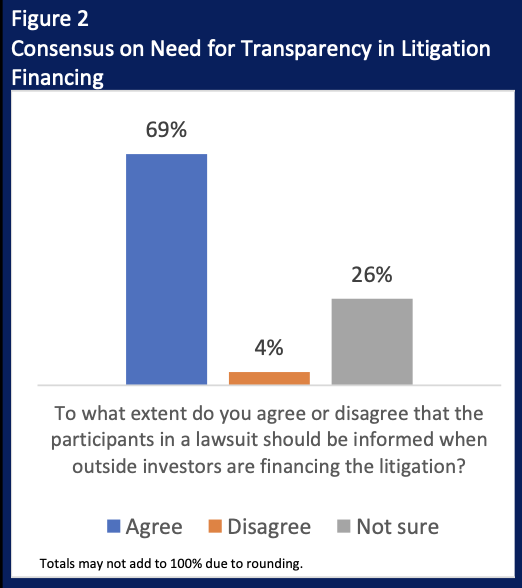
The study reveals the awareness of litigation financing has risen significantly, but most respondents remain neutral in their opinions. Nonetheless, results show consumers want transparency around the involvement of third-party litigation funding in a case. When asked, “To what extent do you agree or disagree that the participants in a lawsuit should be informed when outside investors are financing the litigation,” 69 percent said they agree.
How might increased attorney advertising fuel legal system abuse?
IRC’s findings support a “significant statistical correlation between whether respondents consulted an attorney and their exposure to advertising. Among those who reported seeing attorney advertising, 74 percent consulted an attorney, compared to 48 percent among those who had not seen attorney advertising.”
The American Tort Reform Association (ATRA) estimates that in 2023, over $2.4 billion was spent on local legal services advertising through television, radio, print ads, and billboards across the United States. Meanwhile, only 47 percent of respondents in a 2023 American Bar Association (ABA) survey said their firm had an annual marketing budget – a decline from 57 percent in 2022. About 80 percent of the solo practitioners in the study did not have a marketing budget, and only 31 percent of firms of 2-9 lawyers had one.
Therefore, excessive advertising isn’t universal across the legal industry, and the saturation of advertising channels can more likely be attributed to large firms reaping substantial profits from certain practice areas or firms bolstered by third-party litigation financing. In many instances, both of these conditions factors may be involved. For example, data that ranks the leading legal services advertisers in the United States in 2023 by spending reveals a list dominated by large law firms and attorney conglomerates specializing in mass tort, accident, and personal injury litigation.
The Wall Street Journal reported earlier this year on the ties between advertising surge and the growth in mass product-liability and personal-injury cases, along with the rising involvement from a particular segment of the investment industry in these types of litigation. Nearly 800,000 television advertisements for mass tort cases ran in 2023, costing over $160 million. According to the WSJ, the ads shown most frequently that year included those soliciting individuals who might have been exposed to contaminated water at the Camp Lejeune Marine base. This particular mass tort ranks high on the previously mentioned list of top spenders.
The average dollar amount of third-party litigation funder (TPLF) loans provided to individual law firms ranges from $20 million to $100 million. Given that prospective returns for TPLF loans reportedly reach as high as 20 percent for the riskier mass tort litigation, connecting the surge in advertising for recruiting plaintiffs to the TPLF cash stream may not be such a big leap. Yet, over the years, studies have shown that attorney involvement can increase claims costs and the time needed to resolve them, even while reducing value for claimants.
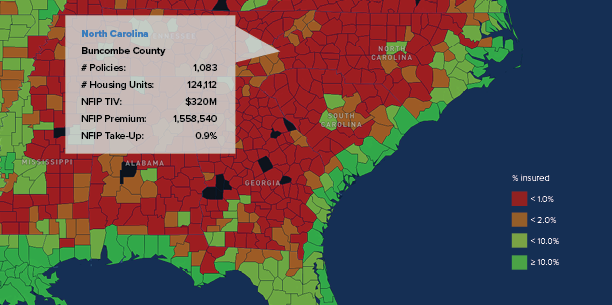
Insurance claims litigation is a growing concern in several states, including Georgia, Louisiana, and Florida, threatening coverage affordability and availability. In Georgia, for example, data indicates that auto coverage affordability for Georgians has been waning faster than in any other state. An August 2024 report, Personal Auto Insurance Affordability in Georgia, issued by IRC, ranked Georgia 47th in terms of auto insurance affordability, while the state tops the most recent list of places that the American Tort Reform Foundation (ATRF) believes judges in civil cases systematically apply laws and court procedures generally to the disadvantage of defendants.
Triple-I and key insurance industry stakeholders define legal system abuse as policyholder or plaintiff attorney practices that increase costs and time to settle insurance claims, including situations when a disputed claim could have been fairly resolved without judicial intervention. Insurers’ legal costs for claims can mount with the increasing number of lawsuit filings, extended litigation, and outsized jury awards (awards exceeding $10 million).
To join the discussion, register for JIF 2024. Follow our blog to learn more about trends in insurance affordability and availability across the property and casualty market.